Measurement Counter
A3117A: CELL_ASS_CMD_MOC_NOT_INCLUDE_DR_TCHF
A3117C: CELL_ASS_CMD_MTC_NOT_INCLUDE_DR_TCHF
A3117D: CELL_ASS_CMD_ECALL_NOT_INCLUDE_DR_TCHF
A3117E: CELL_ASS_CMD_CALL_REEST_NOT_INCLUDE_DR_TCHF
A3118A: CELL_ASS_CMD_MOC_NOT_INCLUDE_DR_TCHH
A3118C: CELL_ASS_CMD_MTC_NOT_INCLUDE_DR_TCHH
A3118D: CELL_ASS_CMD_ECALL_NOT_INCLUDE_DR_TCHH
A3118E: CELL_ASS_CMD_CALL_REEST_NOT_INCLUDE_DR_TCHH
Description
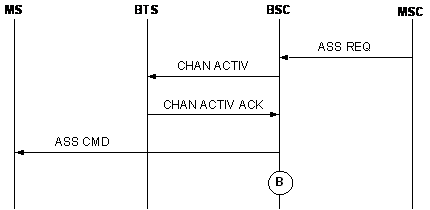
Upon receipt of an ASS REQ message, the BSC assigns a channel based on the channel type specified in the ASS REQ message and then sends a CHAN ACT message to the BTS. If the BSC receives a CHAN ACT ACK message from the BTS, the BSC considers that the channel is successfully activated and so sends an ASS CMD message to the MS. The ASS CMD message carries the information on the ready channel, such as channel type, channel number, and frequency hopping information.
The counters provide the numbers of ASS CMD messages sent by the BSC to the MS based on the MM layer access reason carried in the EST IND message and the channel type specified in the ASS CMD message.
Unit
Integer number or integer.
Measurement Point
As shown in Figure 1, each time the BSC sends an ASS CMD message to the MS (see measurement point B), the corresponding counter is incremented by one based on the MM layer access reason carried in the EST IND message and the channel type specified in the ASS CMD message.
Formula
This is an original counter without involving any formula.