This describes the networking between the BSC and the BTS.
Transmission Modes on the Abis Interface
The following transmission modes can be used on the Abis interface:
- Abis over TDM
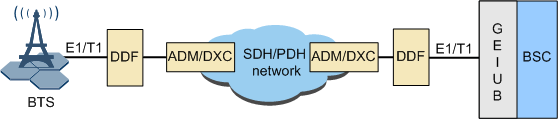
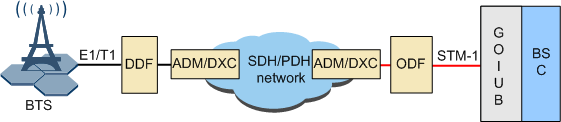
Abis over TDM indicates that the TDM transmission is used on the Abis interface. In this case, the Abis interface board is the GEIUB/GOIUB, and the transmission network between the BSC and the BTS is the SDH/PDH network.
- Abis over HDLC
Abis over HDLC indicates that layer 2 of the Abis interface protocol stack uses the HDLC protocol. In this case, the Abis interface board is the GEHUB, and the transmission network between the BSC and the BTS is the SDH/PDH network.
- Abis over IP
Abis over IP indicates that layer 3 of the Abis interface protocol stack uses the IP protocol. In this case, the Abis interface board is the GFGUB/GOGUB, and the transmission network between the BSC and the BTS is the IP network.
Abis over TDM
In the Abis over TDM networking mode, the Abis interface board in the BSC is the GEIUB/GOIUB. The GEIUB provides E1/T1 electrical ports, and the GOIUB provides STM-1 optical ports.
- Figure 1 shows the E1/T1-based TDM networking on the Abis interface.
- Figure 2 shows the STM-1-based TDM networking on the Abis interface.
If the BTSs connected to the BSC are distributed on different PDH/SDH rings, additional ADM/DXC devices should be used.
Advantages: The networking mode features maturity, flexible QoS, and security. Telecom operators can make full use of the SDH/PDH transmission network resources.
Disadvantages: Compared with the IP transmission networking mode, the cost of this networking mode is high.
Abis over HDLC
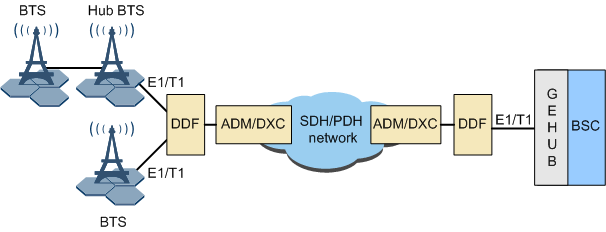
In Abis over HDLC networking mode, the Abis interface board in the BSC is the GEHUB. The GEHUB provides E1/T1 electrical ports. The BSC can be connected to the BTS in HDLC transmission mode or to the Hub BTS.
Figure 3 shows the E1/T1-based HDLC networking on the Abis interface.
Advantages: If the networking mode is used, the utilization of the transmission resources over the Abis interface is improved without reconstruction of the existing SDH/PDH networks.
Disadvantages: No support the high-speed transmission based on STM-1.
Hybrid Networking (Abis over TDM and Abis over HDLC)
The Abis over TDM and Abis over HDLC networking modes can be used on the Abis interface simultaneously. In this case, the Abis interface supports the following configuration modes:
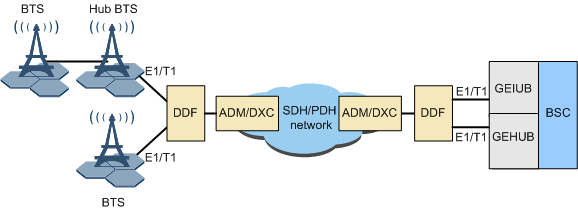
The BSC is configured with the GEIUB/GOIUB and GEHUB. Where, the GEIUB/GOIUB supports TDM transmission and the GEHUB supports HDLC transmission. See Figure 4.
The characteristics of hybrid networking mode are as follows:
- Advantages: If the Abis over HDLC networking mode is used, the utilization of the transmission resources over the Abis interface is improved without reconstruction of the existing SDH/PDH networks.
- Disadvantages: For hybrid combined cabinets and cabinet groups, as some BTSs use HDLC transmission and some use TDM transmission, at least two cables are required to connect the BTS to the BSC. Therefore, transmission resources are wasted.
Abis over IP
In Abis over IP networking mode, the Abis interface adopts the VLAN technology. In other words, signaling and service signals are labeled different VLAN IDs, which are used to differentiate the signaling, voice service signals, and data service signals over the same physical link. Thus, QoS is improved.
In the Abis over IP networking mode, the Abis interface board in the BSC is the GFGUB/GOGUB. The GFGUB provides FE/GE ports,The GOGUB provides GE ports.Based on the transmission networks, the Abis over IP networking modes can be classified into the following types:
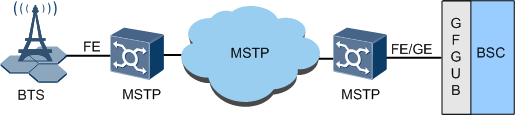
- Figure 5 shows the Multi-Service Transmission Platform (MSTP) based IP networking.
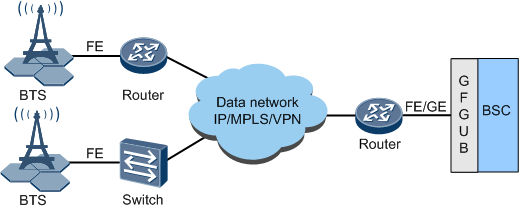
- Figure 6 shows the data-network-based IP networking.
- Applies to the telecom operators that have established the SDH network or MSTP network.
- Provides up to 100 Mbit/s transmission bandwidth through the FE/GE ports, thus facilitating the BTS upgrade and capacity expansion.
- Provides the VC trunk function, which enables the establishment of two VC trunk links between the BTS and the BSC and ensures the security of data transmission. These two links can be used to transmit real-time service data and non-real-time service data.
Disadvantages of MSTP-based IP networking: The MSTP network does not support the evolution from telecommunication networks to IP networks.
- Provides large-capacity bandwidth and reliable transmission on the Abis interface
- Supports the evolution from GSM networks to IP networks
Disadvantages of data-network-based IP networking: cannot ensure good QoS. The end-to-end QoS mechanism must be adopted.