The BSC alarm management involves monitoring the operating status of the BSC and reporting alarm information in real time. Therefore, you can take appropriate measures in time.
BSC Alarm Management
The BSC alarm management has the following functions:
Alarm filtering
The BSC can filter the repetitive fault alarms, recovery alarms, and event alarms.
Alarm shielding
Operators can shield an alarm by alarm ID. Alternatively, they can shield a specific alarm or all alarms of a cell, BTS, or board by setting alarm shielding conditions, thus reducing the number of reported derivative alarms.
Alarm alert
When a fault alarm occurs, the BSC can notify the operators by Email, icon flash, phone, short message, terminal sound, audible and visual indication of alarm box.
Alarm information processing
You can browse alarm information in real time, query history alarm information, and handle alarms based on the handling suggestions available from the online help of the BSC. The BSC can store 100, 000 pieces of history alarm information generated in the latest 90 days.
BSC Alarm Management Mechanism
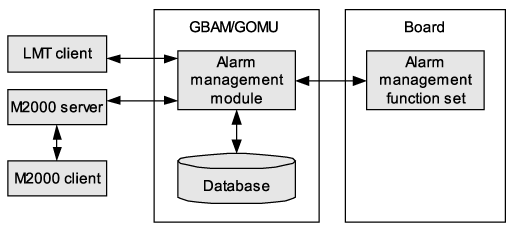
The alarm management process consists of alarm generation, alarm reporting, and alarm handling. Figure 1 shows the alarm management process of the BSC.
Each board detects and reports alarms to the GBAM/GOMU automatically. The GBAM/GOMU classifies these alarms into different levels and sends them to the LMT or to the M2000 server. You can manage the alarms using the LMT or the M2000 client.
The alarm management module of the GBAM/GOMU performs the following functions:
Alarm storage
The alarm management module of the GBAM/GOMU stores the alarms reported by each board in the GBAM/GOMU alarm database.
Alarm processing
The alarm management module of the GBAM processes the operation commands from the LMT or M2000 client. There commands include querying active alarms, querying alarm logs, and modifying alarm configuration items.
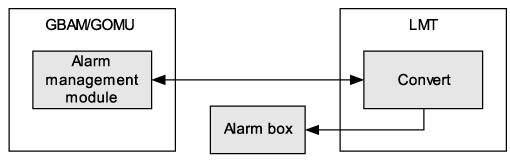
Driving of the Alarm Box
The alarm box generates audible and visual alarms. The red, orange, yellow, and green alarm indicators on the alarm box corresponds to the critical, major, minor, and warning alarms. Different alarm severity levels have different alarm sounds. Figure 2 shows the working principle of the alarm box that is connected to the LMT.
The alarm box is connected to the LMT or GBAM/GOMU/M2000 through the serial port. When an alarm is reported, the alarm forward management module in the LMT instructs the alarm box to generate an audible and visual alarm. You can stop alarm sounds, disable alarm indicators, and reset the alarm box through the LMT.
One LMT can be connected to only one alarm box.