VLM, the network client provided with Novell NetWare version 4.x, provides the same support and behavior under Windows 95 as it does under MS-DOS or Windows 3.1. In addition, you gain the benefits described in "Microsoft Client for NetWare Networks: The Benefits" earlier in this chapter.
If the computer is using VLM, you should still load the Novell-supplied client components and TSR programs, and log on from either AUTOEXEC.BAT or STARTNET.BAT. Login scripts also work in the same way they do with MS-DOS and Windows 3.x. After Windows 95 starts, you can use the Windows 95 user interface to make drive and printer connections, or you can run NetWare utilities by running NWUSER or other commands at the command prompt. Notice, however, that you cannot use NDS names in Windows 95 dialog boxes.
Installing Windows 95 with the VLM client requires special steps if an earlier version of Windows is not installed, as described in this section. This section also presents specific notes related to using the Novell-supplied NetWare 4.x client software with Windows 95.
If you install Windows 95 into the existing Windows directory on a computer where VLM is already configured to run with an earlier version of Windows, then to install VLM support, follow the steps described in "Installing Windows 95 with a Novell NetWare Client" earlier in this chapter.
However, if you are installing Windows 95 into a new directory, or if you are installing it on a computer that has only the MS-DOS operating system (but no earlier version of Windows), you must follow special steps to set up the computer properly. This is because Windows support for VLM requires software supplied only through the Novell-supplied VLM installation program. Follow the instructions under the procedure in this section that most closely describes your configuration.
Windows 95 Setup tries to detect VLM by looking for an NLS directory. If NLS is present, it begins installing Windows 95 for VLM. If the NLS directory is not present but you select the VLM client to install in Setup, Windows 95 Setup asks you to first install VLM using the Novell installation program. Then you can continue with Windows 95 Setup.
Important Automatic logon for the NetWare network from AUTOEXEC.BAT needs to be configured before running Windows 95 Setup; otherwise, your login script will not be run under Windows 95 (and therefore any mapped drives will not be available).
– Or –
Note If you were logged into NDS when Setup was started, then VLM appears in this list and you can skip the following steps.
Setup partially configures Windows 95, and then prompts you to run the Novell Workstation Shell Install program after Windows 95 has been installed.
Note Setup also places the entry device=vnetbios in SYSTEM.INI, which causes a blue screen to appear when you restart the computer. You can ignore this screen.
In the Network option in Control Panel, you will see that Setup has added Novell NetWare (Workstation Shell 4.0 And Above [VLM]) as a network client. Information in NET.CFG is used to configure the other network components.
For information about required files, see "Obtaining Current Novell-Supplied Files" later in this chapter.
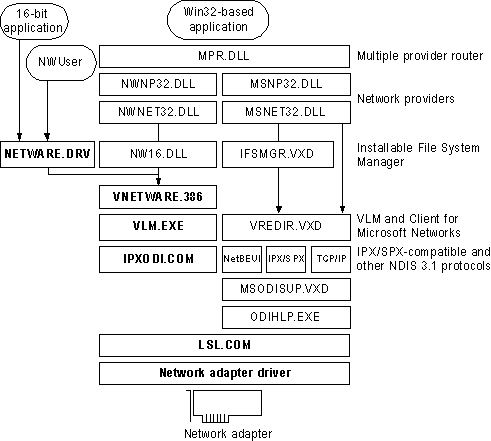
If you are using VLM as the network client, you might also choose to install the 32-bit, protected-mode Client for Microsoft Networks if you want to connect to other Microsoft networking computers, such as computers running Windows for Workgroups 3.x, LAN Manager, or Windows NT. The following illustration describes this configuration.
Architecture for Novell-supplied VLM with Client for NetWare Networks; Components shown in bold are supplied by Novell.

In this configuration, the Novell-supplied version of NETWARE.DRV is not used by Windows 95. It is installed and loaded only for applications that call it directly. All access to NetWare resources is through the Windows 95 user interface, not the NETWARE.DRV dialog boxes. The NWUSER utility calls NETWARE.DRV directly to bring up the central NetWare Version 3.0 WinNet16 dialog box.
Notice that this configuration requires a Microsoft Windows NT Client Access License if this computer will be connecting to servers running Windows NT Server. For more information, see Chapter 8, "Windows 95 on Microsoft Networks."
This configuration can be used if you do not need to connect to other computers that are running Windows for Workgroups 3.x, LAN Manager, or Windows NT. (Of course, you can connect to a Windows 95 computer running Microsoft File and Printer Sharing for NetWare.)
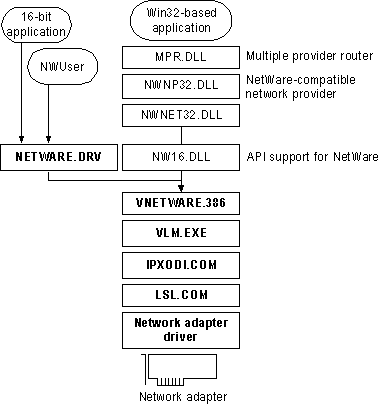
The following illustration summarizes this configuration.
Architecture for Novell-supplied VLM as the sole client; Components show in bold are supplied by Novell.
The following table lists the required settings for CONFIG.SYS and AUTOEXEC.BAT files if you use VLM as the sole network client.
Configuration File Settings for VLM as the Sole Client
Filename | Required settings |
config.sys | lastdrive=drive_letter |
autoexec.bat | startnet.bat |
startnet.bat | lsl.com |
The following table summarizes the minimum settings that you should see in the Network option in Control Panel if you install Windows 95 with VLM as the sole client.
Network Settings for VLM as the Sole Client
Network component | Options |
NetWare (Workstation Shell 4.X [VLM]) | Novell NetWare (Workstation Shell 4.X [VLM]) appears in the list of installed components. All other settings are configured in NET.CFG. |
Network adapter | In the General properties for the adapter, the Real Mode (16-bit) ODI Driver option should be checked. |
Novell IPX ODI | Settings are configured in NET.CFG. |
Windows 95 uses the value of the LastDrive= entry in the Registry to allocate enough storage space in the internal memory structures to recognize drive letters for devices. For example, a setting of LastDrive=Z tells Windows 95 to recognize drive letters from A to Z.
The Novell-supplied NetWare 4.x redirector handles the LastDrive= entry the same way that Windows 95 does. That is, both the NetWare 4.x redirector and Windows 95 allow drive letters to be used to connect to redirected network drives up through the drive letter specified by the LastDrive= entry.
The NetWare 4.x redirector uses the First Network Drive= entry in the NET.CFG file to identify the first network drive that can be mapped. For more information about this setting, consult your Novell documentation.