HKEY_CURRENT_USER contains the database that describes the user profile for the user who is currently logged on the local computer. A user profile contains information that defines the appearance and behavior of the individual user's desktop, network connections, and other environment settings. A user profile ensures that Windows NT will look and act the same at any computer where that user logs on, if that person's profile is available at that computer or on the same domain in Windows NT Server.
HKEY_CURRENT_USER contains all the information necessary to set up a particular user environment on the computer. Information such as program groups, application preferences, screen colors, and other personal preferences and security rights are included. Many of these settings are the same kind of information that was stored in the WIN.INI file under Windows for MS-DOS.
HKEY_CURRENT_USER includes the default subkeys described in the following table. For details about managing the hives for user profiles, see "Managing User Profiles through the Registry" in Chapter 12, "Configuration Management and the Registry." For details about the contents of subkeys in HKEY_CURRENT_USER, see "Registry Entries for User Preferences" in Chapter 14, "Registry Value Entries."
Table 10.7 Default Subkeys in HKEY_CURRENT_USER
Subkey | Contents |
Console | Subkeys that define the options and window size for a console (the interface between the user and character-mode applications). This includes settings for the Windows NT command prompt. These settings should be changed by using the commands in the Control menu for each of the specific non-Windows–based applications. (The subkey for the command prompt does not appear unless the font or screen colors have been changed by the current user.) |
Control Panel | Subkeys that have parameters adjusted by applications in Control Panel, for example, the Windows NT Desktop. This includes information that was stored in the WIN.INI and CONTROL.INI files under Windows for MS-DOS. |
Environment | Value entries that correspond to the current user's settings for environment variables. This includes information that was stored in the AUTOEXEC.BAT file under MS-DOS. Values should be set by using the System icon in Control Panel. |
Keyboard Layout | The value entry that gives the current active keyboard layout. This value should be set by using the International icon in Control Panel. |
Printers | Subkeys that describe the printers installed for the current user. These values should be set by using Print Manager. |
Program Groups | Subkeys that describe the names and settings for the current user's program groups. Values defining common program groups are stored in HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\ProgramGroups. Personal program groups should be set by using the menu commands or mouse techniques in Program Manager. |
Software | Subkeys that describe the current user's configurable settings for installed software that the user can use. This information has the same structure as HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE. This information contains application-specific information that was stored in the WIN.INI file or private initialization files under Windows for MS-DOS. |
Whenever similar data exists in HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE and HKEY_CURRENT_USER, the data in HKEY_CURRENT_USER takes precedence, as described earlier, in "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE." The most significant example is environment variables, where variables defined for the user who is currently logged on take precedence over system variables, as defined by using the System icon in Control Panel.
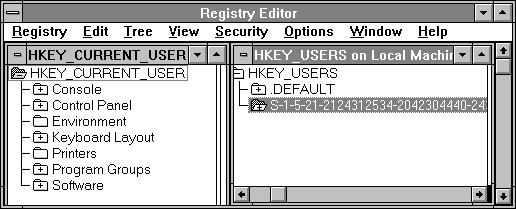
HKEY_CURRENT_USER is mapped to HKEY_USER\SID_#, where SID_# is the Security ID string of the current user, as shown in the following example from Registry Editor. The Windows NT logon process builds a user's personal profile environment based upon what it finds in HKEY_USER\SID_#. If no such data is available, HKEY_CURRENT_USER is built from the data in HKEY_USER\.DEFAULT.
Note To find the name of the file that goes with a hive, see the HiveList subkey in HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control. To find which hive file goes with a user profile (whether or not the user is logged on), see the ProfileList subkey under HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion. You can use the Find Key command from the View menu in Registry Editor to locate a specific key quickly.
