Although TCP/IP uses IP addresses to identify and reach computers, users typically prefer to use computer names. DNS is a naming service generally used in the UNIX networking community to provide standard naming conventions for IP workstations. Windows Sockets applications and TCP/IP utilities, such as ftp and telnet, can also use DNS in addition to the HOSTS file to find systems when connecting to foreign hosts or systems on your network.
Contact the network administrator to find out whether you should configure your computer to use DNS. Usually, you can use DNS if you are using TCP/IP to communicate over the Internet or if your private internetwork uses DNS to distribute host information. For information, see "Domain Name System Addressing" in Chapter 12, "Networking Concepts for TCP/IP."
Microsoft TCP/IP includes DNS client software for resolving Internet or UNIX system names. Microsoft Windows networking provides dynamic name resolution for NetBIOS computer names via WINS servers and NetBIOS over TCP/IP.
DNS configuration is global for all network adapters installed on a computer.

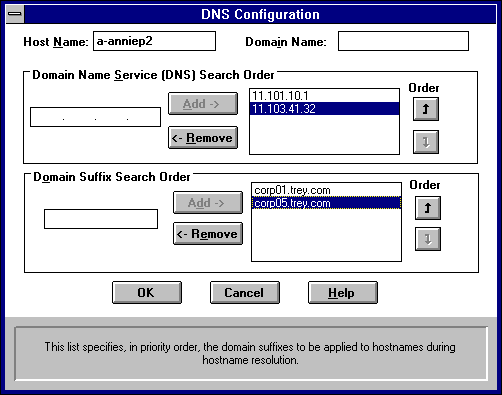
Names are displayed in the Host Name box and Domain Name box.
The host name can be any combination of A–Z letters, 0–9 numerals, and the hyphen (-) character.
Note Some characters that can be used in Windows NT computer names, particularly the underscore, cannot be used in host names.
By default, this value is the Windows NT computer name, but the network administrator can assign another host name without affecting the computer name. The host name is used to identify the local computer by name for authentication by some utilities. Other TCP/IP-based utilities, such as rexec, can use this value to learn the name of the local computer. Host names are stored on DNS servers in a table that maps names to IP addresses for use by DNS.
The DNS Domain Name can be any combination of A–Z letters, 0–9 numerals, and the hyphen (-) plus the period (.) character used as a separator.
The DNS Domain Name is usually an organization name followed by a period and an extension that indicates the type of organization, such as microsoft.com. The DNS Domain Name is used with the host name to create a fully qualified domain name (FQDN) for the computer. The FQDN is the host name followed by a period (.) followed by the domain name. For example, this could be corp01.research.trey.com, where corp01 is the host name and research.trey.com is the domain name. During DNS queries, the local domain name is appended to short names.
Note A DNS domain is not the same as a Windows NT or LAN Manager domain.
The network administrator should provide the correct values for this parameter.
You can add up to three IP addresses for DNS servers. The servers running DNS will be queried in the order listed. To change the order of the IP addresses, select an IP address to move, and then use the up- and down-arrow buttons. To remove an IP address, select the IP address, and then choose the Remove button.
This list specifies the DNS domain suffixes to be appended to host names during name resolution. You can add up to six domain suffixes. To change the search order of the domain suffixes, select a domain name to move, and then use the up- and down-arrow buttons. To remove a domain name, select the domain name, and then choose the Remove button.
The settings take effect after you restart the computer.