Microsoft TCP/IP provides all the elements necessary to implement these protocols for networking. Microsoft TCP/IP includes the following:
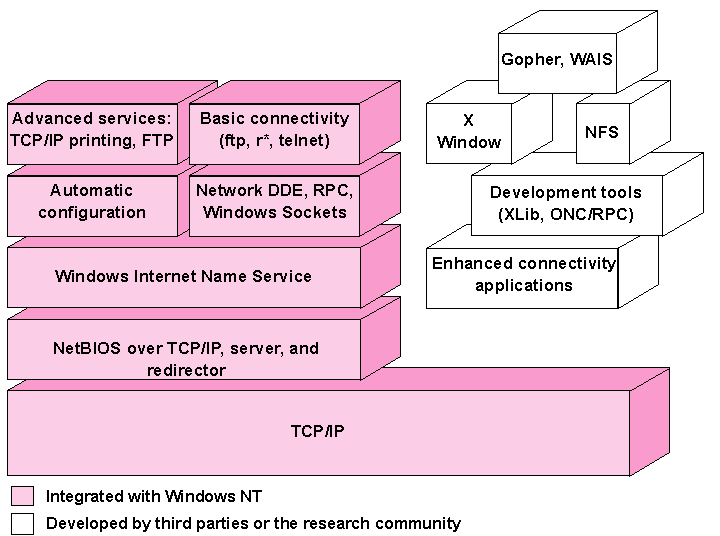
The following figure shows the elements of Microsoft TCP/IP alongside the variety of additional applications and connectivity utilities provided by Microsoft and other third-party vendors.

Figure 10.1 Microsoft TCP/IP Core Technology and Third-party Add-ons
TCP/IP standards are defined in Requests for Comments (RFCs), which are published by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) and other working groups. The relevant RFCs supported in this version of Microsoft TCP/IP (and for Microsoft Remote Access Service) are described in the following table.
Table 10.1 Requests for Comments (RFCs) Supported by Microsoft TCP/IP
RFC | Title |
768 | User Datagram Protocol (UDP) |
783 | Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) |
791 | Internet Protocol (IP) |
792 | Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) |
793 | Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) |
826 | Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) |
854 | Telnet Protocol (TELNET) |
862 | Echo Protocol (ECHO) |
863 | Discard Protocol (DISCARD) |
864 | Character Generator Protocol (CHARGEN) |
865 | Quote of the Day Protocol (QUOTE) |
867 | Daytime Protocol (DAYTIME) |
894 | IP over Ethernet |
919, 922 | IP Broadcast Datagrams (broadcasting with subnets) |
959 | File Transfer Protocol (FTP) |
1001, 1002 | NetBIOS Service Protocols |
1034, 1035 | Domain Name System (DOMAIN) |
1042 | IP over Token Ring |
1055 | Transmission of IP over Serial Lines (IP-SLIP) |
1112 | Internet Gateway Multicast Protocol (IGMP) |
1122, 1123 | Host Requirements (communications and applications) |
1134 | Point to Point Protocol (PPP) |
1144 | Compressing TCP/IP Headers for Low-Speed Serial Links |
1157 | Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) |
1179 | Line Printer Daemon Protocol |
1188 | IP over FDDI |
1191 | Path MTU Discovery |
1201 | IP over ARCNET |
1231 | IEEE 802.5 Token Ring MIB (MIB-II) |
1332 | PPP Internet Protocol Control Protocol (IPCP) |
1334 | PPP Authentication Protocols |
1533 | DHCP Options and BOOTP Vendor Extensions |
1534 | Interoperation Between DHCP and BOOTP |
1541 | Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) |
1542 | Clarifications and Extensions for the Bootstrap Protocol |
1547 | Requirements for Point to Point Protocol (PPP) |
1548 | Point to Point Protocol (PPP) |
1549 | PPP in High-level Data Link Control (HDLC) Framing |
1552 | PPP Internetwork Packet Exchange Control Protocol (IPXCP) |
1553 | IPX Header Compression |
1570 | Link Control Protocol (LCP) Extensions |
Draft RFCs | NetBIOS Frame Control Protocol (NBFCP); PPP over ISDN; PPP over X.25; Compression Control Protocol |
All RFCs can be found on the Internet via ds.internic.net.
In this version of Windows NT, Microsoft TCP/IP does not include a complete suite of TCP/IP connectivity utilities, Network File System (NFS) support, or some TCP/IP server services (daemons) such as routed and telnetd. Many such applications and utilities that are available in the public domain or from third-party vendors are compatible with Microsoft TCP/IP.
Tip For Windows for Workgroups computers and MS-DOS–based computers on a Microsoft network, you can install the new version of Microsoft TCP/IP—32 for Windows for Workgroups and the Microsoft Network Client version 2.0 for MS-DOS from the Windows NT Server 3.5 compact disc. This software includes the DHCP and WINS clients and other elements of the new Microsoft TCP/IP software. For information about installing these clients, see Chapter 9, "Network Client Administrator," in the Windows NT Server Installation Guide.