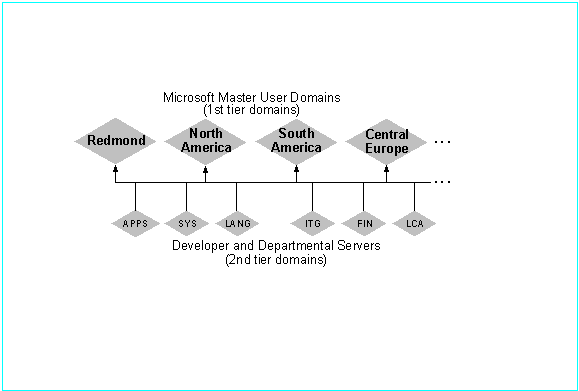
Again, Microsoft employs the multiple master domain strategy. Because every user and global group account in the company exists in one of the master user domains, and because all the domains in the company trust every master user domain, every user and global group account in the company is functional in all domains.
In all cases, ITG has full administrative permissions on all the domains in the model. This is so that all domain controllers can be backed up and restored, and updated with current builds and new system configuration files.
There are some disadvantages to this model. The most challenging issue is administration of individualized global groups. Creation and administration of global groups becomes impractical to manage unless it can be done based on a database against which data can be compared. This allows for an automatic update if an individual no longer requires membership in that group. ITG provides global groups based on department accounts, and updates membership based on HR records. Additional global groups are reviewed on a case-by-case basis. Users are added to a master user domain based on their current geographic location. If a user moves to a different site within Microsoft (for example, Redmond to Northern Europe), he/she will be removed and added to the appropriate master user domain.
Windows for Workgroup-based systems belong to a second-tier domain to ensure that they have full access to the domain model. They use their account on the master user domain and use the second-tier domain as their workgroup. This allows them to access servers in the domain that are using Windows NT security.
All Windows NT Server-based systems running Remote Access Services (RAS) are located in a second-tier domain. Because there is a trust relationship between all the domains in the corporate model, a user can dial into any RAS server anywhere in the model without needing additional administration.
ITG has sole authority to establish a trust relationship between the master domains and another domain on the Microsoft corporate network. ITG has administrative ability on all servers running Windows NT Server in a trust relationship within the Microsoft domains structure.
Microsoft ITG uses the following criteria to establish a trust relationship with a second-tier domain:
The master user account domains contain all the user accounts for the entire domain structure worldwide. Master user domain names represent the geographic location of users to assist in distribution of backup domain controllers.

Microsoft Domain Model
Two categories of administration are acknowledged at Microsoft. ITG is solely responsible for administration of some domains. Other domains are jointly administered by ITG and specific user groups, such developers, sites, and others. Domain administration permissions can be given to a group of users within their second-tier domain. ITG retains the option of allowing any of the departmental server domains to have their own domain administrators and ITG administration.