A gateway can handle the transfer of Microsoft Exchange Server special properties across a backbone by encapsulating the message so that these properties pass through the foreign system and remain intact at its destination. Microsoft Exchange Server encapsulates message parts by encoding them in TNEF. For more information, see Transport Neutral Encoding Format.
The gateway should determine which recipients of the message are MAPI-Recipients, and then encapsulate MAPI message parts for transfer to those recipients. The gateway maps the message to the foreign systemís format and stores the messageís content in a TNEF encapsulated attachment in the foreign systemís attachment format.
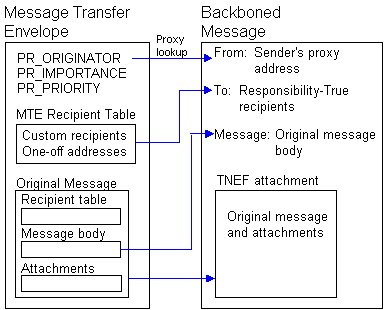
The following figure shows how addresses and message content are backboned using encapsulation.

Encapsulating a message for backboning
The message transfer envelope (MTE) contains information that is necessary for a message to pass through the foreign system. Envelope information must be preserved during the backboning process so a backboned message can be delivered intact to the destination Microsoft Exchange Server system by the receiving gateway.
Your gateway can encapsulate message attachments in two ways:
See Message Transfer for more information about message transfer envelopes and transferring message properties.