In some cases, Microsoft Exchange Server is installed within an organization that uses other messaging systems such as SMTP and X.400. Objects such as mail recipients that are defined within these messaging systems are sometimes referred to as external objects. They can be addressed from within the Microsoft Exchange Server messaging environment in two ways:
Because every addressable directory object has a distinguished name (DN) consisting of its path plus its name, applications can address a message to any object using the objectís DN, regardless of whether an object is internal or external to the Microsoft Exchange Server environment. If an external object is referred to by its DN, Microsoft Exchange Server will automatically resolve the DN to the appropriate external address. This resolution is done using the Target-Address attribute, which is defined on all custom recipient objects.
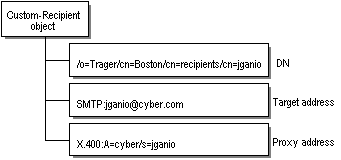
The Target-Address attribute indicates the default external address to use for an object. A Target-Address is usually an X.400, SMTP, or other external address. All addressable objects in the directory also contain a set of proxy address attributes, each of which contains the address of the object represented in a foreign mail system. Proxy addresses make it possible to address any object using several addressing schemes, and also to send mail to a user in a foreign system using the proxy address in the Microsoft Exchange Server system. The concepts described in this section are illustrated in the following figure, which shows a Custom-Recipient object and three of its addressing attributes.

Custom recipient object with three addressing attributes