Microsoft SQL Enterprise Manager is a graphical tool¾included as part of Microsoft SQL Server 6.0¾that provides an intuitive way to administer SQL Servers enterprise-wide.
SQL Enterprise Manager provides powerful administration tools for managing multiple servers. A new scheduling engine enables you to schedule tasks to run automatically at a specified time, completely unattended. A new alert engine enables you to set alerts for various SQL Server events and either notify someone, through email or paging, or automatically execute a task. Additionally, a replication service enables you to set up and administer replication for SQL Servers across your network.
SQL Enterprise Manager is installed by the setup program as part of the server software on Windows NT-based computers, and as part of the client software on Windows NT- and Windows 95-based computers. (Because SQL Enterprise Manager is a 32-bit application, it cannot be installed on computers running 16-bit operating systems.) You start SQL Enterprise Manager by choosing its icon from the Microsoft SQL Server 6.0 program group.

When you start SQL Enterprise Manager, it looks like this:
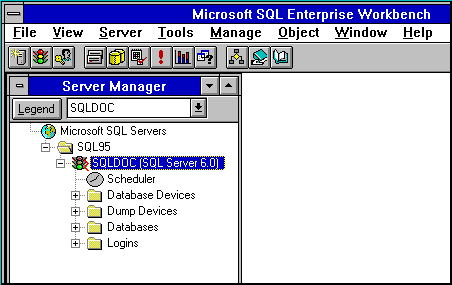
Anyone who can access SQL Server can use SQL Enterprise Manager; no explicit permission is needed. Access to the objects and tasks within SQL Enterprise Manager is controlled by the permissions of the login identification. If the user logs in as system administrator (SA), then that user can access all tasks and objects. If a user is the database owner (DBO), then that user can access those tasks and objects the DBO has permission for. Any user can access all objects he or she has created and perform whatever other tasks he or she has permission for.
With SQL Enterprise Manager you can:
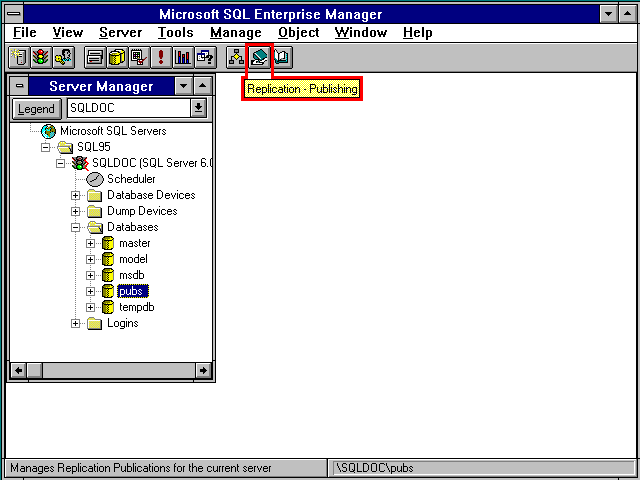
You can administer these SQL Server tasks using the menus in SQL Enterprise Manager or the toolbar buttons. When you point to a button and pause for a moment, the name of the button appears in a ToolTip, as shown here for the Replication - Publishing button.
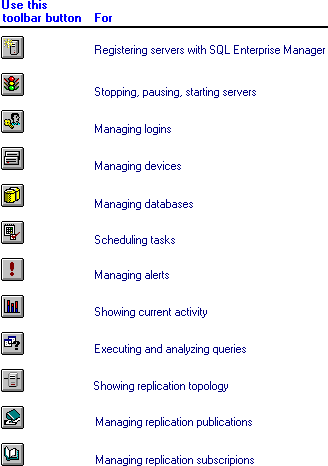
For more information, see The Server Manager Window.