Starting SQL Server Using SQL Service Manager
 To start SQL Server using SQL Service Manager
To start SQL Server using SQL Service Manager
-
From the Microsoft SQL Server 6.0 program group, start SQL Service Manager.
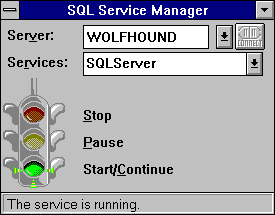
The SQL Service manager window appears:
-
If the service is a remote service, select or enter the remote server name in the Server box, and then choose the Connect button.
This connects you to the remote server and fills the Services box with the names of the SQL Server services that are registered on the remote computer. Note that the Server box appears only if the Remote Control option on the System menu (opened by choosing the "-" box in the upper left-hand corner of the window) is turned on.
-
In the Services box, select MSSQLServer.
The current state of the service is indicated by the light on the traffic signal and by the message in the status bar.
-
Choose the green Start/Continue light.
-
If a confirmation box appears, choose the Yes button.
SQL Server starts as a service under the Windows NT Service Control Manager using the default startup options written to the Windows NT Registry by the setup program.
You can also stop, pause and continue SQL Server by using the same procedure used to start the service. To stop the service, select the red light, to pause the service, select the yellow light, to continue a paused service, select the green light.
The SQL Service Manager System menu (opened by choosing the "-" box in the upper left-hand corner of the window) includes these options:
-
Action Verify
-
Indicates whether you want the SQL Service Manager to present a confirmation box before stopping, pausing, starting, or continuing a service, including dependent services such as SQL Executive. (For details about the dependencies between SQL Server and SQL Executive, see Running SQL Executive.)
-
Remote Control
-
Indicates whether you want the SQL Service Manager window to include the Server box for controlling services on remote servers.
-
Polling Interval
-
Displays the Polling Interval dialog box, which is used to set how often the state of the service (SQL Server or SQL Executive) is checked.
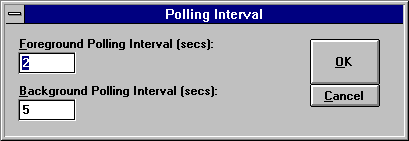
The Polling Interval dialog box contains two options:
-
The Foreground Polling Interval (secs.)
-
Sets the polling interval, in seconds, for the SQL Service Manager when it is running in the foreground (not minimized). The default is 2.
-
Background Polling Interval (secs.)
-
Sets the polling interval, in seconds, for the SQL Service Manager when it is running in the background (minimized). The default is 5.
 To start SQL Server using SQL Service Manager
To start SQL Server using SQL Service Manager To start SQL Server using SQL Service Manager
To start SQL Server using SQL Service Manager
