Shading and color effects control the display of faces in a model.
The face style defines the shading on a face. Real (below left) is meant to produce the effect of realism. Gooch (below right) can show details better by softening the contrast between lighted areas and shadowed areas. Lighted areas use warm tones and darker areas cool tones.
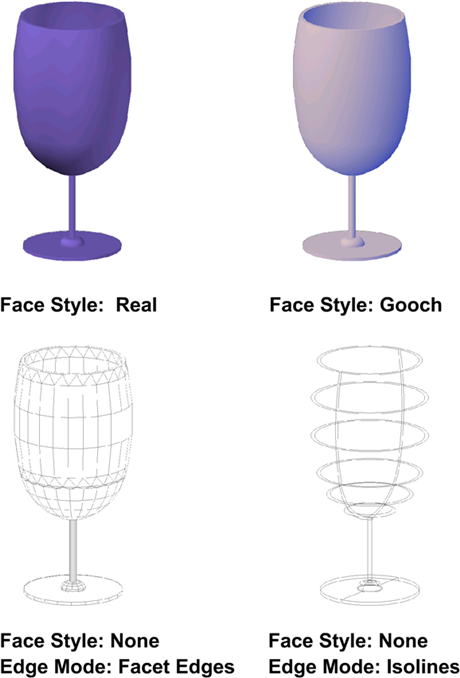

When the None face style is active, there is no shading, and only edges are displayed if Edge Mode is set to Facet Edges or Isolines under Edge Settings.
Faceted lighting computes a single color for each face. Objects appear flatter. Smooth lighting smoothes the edges between polygon faces by computing the colors as a gradient between the vertexes of the faces. This gives the objects a smooth appearance. For the smoothest option, the Per-Pixel Lighting setting needs to be turned on in the Manual Performance Tuning Dialog Box. The colors are computed for individual pixels and gives a smoother appearance. If not, the smooth setting is used instead.

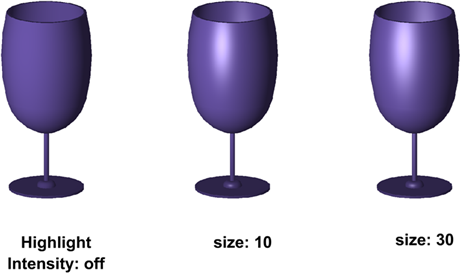
The size of the highlights on an object affects the perception of shininess (below). A smaller, more intense highlight makes objects look shinier. The highlight intensity that is set in a visual style does not apply to objects with materials attached.
Color can be displayed in the normal way, or you can change the face color mode. Monochrome displays all faces in the same color and shaded. Tint uses the same color to shade all faces by changing the hue and saturation values of the color. Desaturate mode softens colors.