Basic mesh forms such as boxes, cones, cylinders, pyramids, wedges, spheres, and tori.
Any view where the UCS icon appears in rendered colored form; current visual style is not 2D Wireframe, and the model is being viewed from an isometric view.
Coordinate values measured from a coordinate system's origin point. See also origin, relative coordinates, user coordinate system (UCS), world coordinates, and world coordinate system (WCS).
In the tracking or object snap tracking methods of locating a point, an intermediate location used as a reference.
During tracking or object snap tracking, the temporary plus sign displayed at the location of an acquired point.
The smallest task or user interaction that can be recorded with the Action Recorder.
Toolbar-like UI that displays the actions associated with a parameter object.
A series of recorded actions that can be played back in the active drawing.
A file that stores all the actions contained in an action macro. Action macro files have the file extension .actm.
A control used to display the recorded actions in an action macro.
Part of the Autodesk software registration process. It allows you to run a product in compliance with the product's end-user license agreement.
A method of controlling performance that turns off features in a certain order when performance falls below a specified level.
A method to accelerate the anti-aliasing process within the bounds of the sample matrix size. See also anti-aliasing.
A selection of table cells that share at least one boundary with another cell in the same selection.
A tablet calibration method that provides an arbitrary linear transformation in two-dimensional space. Affine calibration requires three calibration points to allow a tablet transformation that combines translation, independent X and Y scaling, rotation, and some skewing. Use affine calibration if a drawing has been stretched differently in the horizontal or vertical direction. (TABLET)
A shortcut for a command. For example, CP is an alias for COPY, and Z is an alias for ZOOM. You define aliases in the acad.pgp file.
The effect of discrete picture elements, or pixels, aligned as a straight or curved edge on a fixed grid appearing to be jagged or stepped. See also anti-aliasing.
A dimension that measures the distance between two points at any angle. The dimension line is parallel to the line connecting the dimension's definition points. (DIMALIGNED)
Alpha is a type of data, found in 32-bit bitmap files, that assigns transparency to the pixels in the image.
A 24-bit truecolor file contains three channels of color information: red, green, and blue, or RGB. Each channel of a truecolor bitmap file is defined by 8 bits, providing 256 levels of intensity. The intensity of each channel determines the color of the pixel in the image. Thus, an RGB file is 24-bit with 256 levels each of red, green, and blue.
By adding a fourth, alpha channel, the file can specify the transparency, or opacity, of each of the pixels. An alpha value of 0 is transparent, an alpha value of 255 is opaque, and values in between are semi-transparent. An RGBA file (red, green, blue, alpha) is 32-bit, with the extra 8 bits of alpha providing 256 levels of transparency.
To output a rendered image with alpha, save in an alpha-compatible format such as PNG, TIFF, or Targa.
A color produced only by ambient light. Ambient color is the color of an object where it is in shadow. This color is what the object reflects when illuminated by ambient light rather than direct light.
Light that illuminates all surfaces of a model with equal intensity. Ambient light has no single source or direction and does not diminish in intensity over distance.
A dimension that measures angles or arc segments and consists of text, extension lines, and leaders. (DIMANGULAR)
The unit of measurement for an angle. Angular units can be measured in decimal degrees, degrees/minutes/seconds, grads, and radians.
A setting that is saved with model space, layout viewports, and model views. When you create annotative objects, they are scaled based on the current annotation scale setting and automatically displayed at the correct size.
Dimensional constraint used to control the size of the geometry as well as annotate the drawing.
See also parameter constraint, and dynamic constraint
Text, dimensions, tolerances, symbols, notes, and other types of explanatory symbols or objects that are used to add information to your model.
A property that belongs to objects that are commonly used to annotate drawings. This property allows you to automate the process of scaling annotations. Annotative objects are defined at a paper height and display in layout viewports and model space at the size determined by the annotation scale set for those spaces.
An unnamed block created by a number of features, including associative and nonassociative dimensions.
A method that reduces aliasing by shading the pixels adjacent to the main pixels that define a line or boundary. See also aliasing.
The button that is displayed in the top-left corner of the application. If you click the application button, the application menu is displayed.
The menu that is displayed when you click the application button. The application menu contains common tools for creating, saving, and publishing a file.
Point locations that a B-spline must pass near, within a fit tolerance. See also fit points and interpolation points.
1. Multiple copies of selected objects in a rectangular or polar (radial) pattern. (ARRAY) 2. A collection of data items, each identified by a subscript or key, arranged so a computer can examine the collection and retrieve data with the key.
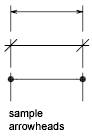
A terminator, such as an arrowhead, slash, or dot, at the end of a dimension line showing where a dimension begins and ends.
Ratio of display width to height.
A dimension that automatically adapts as the associated geometry is modified. Controlled by the DIMASSOC system variable. See also nonassociative dimension and exploded dimension.
Hatching that conforms to its bounding objects such that modifying the bounding objects automatically adjusts the hatch. (BHATCH)
The diminishing of light intensity over distance.
An object that is included in a block definition to store alphanumeric data. Attribute values can be predefined or specified when the block is inserted. Attribute data can be extracted from a drawing and inserted into external files. (ATTDEF)
A text file to which extracted attribute data is written. The contents and format are determined by the attribute extraction template file. See also attribute extraction template file.
A text file that determines which attributes are extracted and how they are formatted when written to an attribute extraction file. See also attribute extraction file.
The text string displayed when you insert a block with an attribute whose value is undefined. See also attribute definition, attribute tag, and attribute value.
A text string associated with an attribute that identifies a particular attribute during extraction from the drawing database. See also attribute definition, attribute prompt, and attribute value.
The alphanumeric information associated with an attribute tag. See also attribute definition, attribute prompt, and attribute tag.
The order in which looks for a support file: current directory, drawing directory, directory specified in the support path, and directory containing the executable file, acad.exe.
The drawing area, its surrounding menus, and the command line.
Icon with X, Y, and Z coordinates that is used to visualize the viewpoint (view direction) of a drawing without displaying the drawing. (VPOINT)
A blended piecewise polynomial curve passing near a given set of control points. See also Bezier curve. (SPLINE)
The opposite side of a front face. Back faces are not visible in a rendered image. See also front faces.
1. In the context of editing grips, the grip that changes to a solid color when selected to specify the focus of the subsequent editing operation. 2. A point for relative distance and angle when copying, moving, and rotating objects. 3. The insertion base point of the current drawing. (BASE) 4. The insertion base point for a block definition. (BLOCK)
An imaginary line on which text characters appear to rest. Individual characters can have descenders that drop below the baseline. See also baseline dimension.
Multiple dimensions measured from the same baseline. Also called parallel dimensions. See also baseline.
Displays a brief description for the tooltip.
A reference to the View Object wheel and Tour Building wheel.
A polynomial curve defined by a set of control points, representing an equation of an order one less than the number of points being considered. A Bezier curve is a special case of a B-spline curve. See also B-spline curve.
The large version of the SteeringWheels. Labels are displayed on each wheel wedge and they are larger than the size of the cursor.
The digital representation of an image having bits referenced to pixels. In color graphics, a different value represents each red, green, and blue component of a pixel.
Temporary screen markers displayed in the drawing area when you specify a point or select objects. (BLIPMODE)
A generic term for one or more objects that are combined to create a single object. Commonly used for either block definition or block reference. See also block definition and block reference. (BLOCK)
Defines how the geometry of a dynamic block reference will move or change when the custom properties of a block reference are manipulated in a drawing. A dynamic block definition usually contains at least one action that is associated with a parameter. (BACTION)
A dimensional constraint, parameter, or action that adds intelligence to a block definition.
Tool palettes used in the Block Editor to add actions and parameters to dynamic block definitions.
Actions, parameters, and parameter sets on the tabs of the Block Authoring Palettes window. Used in the Block Editor to create dynamic blocks.
A dimensional constraint that has block authoring information associated with it.
See also: dynamic constraint
See also: annotational constraint
The name, base point, and set of objects that are combined and stored in the symbol table of a drawing. See also block and block reference.
The nongraphical data area of a drawing file that stores block definitions. See also named object.
See block reference.
A table that enables users to define different values for a set of properties for the block definition. Replacement for lookup properties in the future.
A compound object that is inserted in a drawing and displays the data stored in a block definition. Also called instance. See also block and block definition. (INSERT)
A closed area that consists of a single object (such as a circle) or of multiple, coplanar objects that overlap. You can insert hatch fills within bounded areas.
Bounded areas are also used to create 3D objects through extrusion by using the PRESSPULL command.
A map in which brightness values are translated into apparent changes in the height of the surface of an object.
The menu for a pointing device with multiple buttons. Each button on the pointing device (except the pick button) can be defined in the customization file (acad.cui).
A special object property used to specify that the object inherits the color or linetype of any block containing it. See also BYLAYER.
A special object property used to specify that the object inherits the color or linetype associated with its layer. See also BYBLOCK.
A block used as symbol to reference another sheet. Callout blocks have many industry-specific terms, such as reference tags, detail keys, detail markers, and so on. See also label block.
Defines the current eye-level position in a 3D model. A camera has a location XYZ coordinate, a target XYZ coordinate, and a field of view or lens length, which determines the magnification or zoom factor.
Defines the point you are viewing by specifying the coordinate at the center of the view.
The SI unit of luminous intensity (perceived power emitted by a light source in a particular direction) (Symbol: cd). Cd/Sr
See view category.
The smallest available table selection.
The four gridlines surrounding a table cell. An adjacent cell selection can be surrounded with a cell boundary.
A style that contains specific formatting for table cells.
In a dynamic block definition, a property of point, linear, polar, XY, and rotation parameters. When set to Yes, a change in an action that contains the parameter in the action's selection set triggers any actions associated with that parameter, just as if you had edited the parameter in the block reference through a grip or custom property.
An externally referenced drawing (xref) that references itself directly or indirectly. The xref that creates the circular condition is ignored.
The boundaries that define or clip the field of view.
For cyan, magenta, yellow, and key color. A system of defining colors by specifying the percentages of cyan, magenta, yellow, and the key color, which is typically black.
Increases or decreases the saturation of the reflected color from the material.
A table defining the intensity of red, green, and blue (RGB) for each displayed color.
A vertically adjacent table cell selection spanning the height of the table. A single column is one cell in width.
A text area reserved for keyboard input, prompts, and messages.
A visual aid that indicates the directions North, South, East, and West in the current model.
A solid created from two or more individual solids. (UNION, SUBTRACT, INTERSECT)
Displays the geometric constraints associated with objects or with points on objects.
Point on an object that can be geometrically and/or dimensionally constrained (for example, an endpoint or an insertion point).
Form of parametric design.
Rules that govern the position, slope, tangency, dimensions, and relationships among objects in a geometry.
See workplane.
A ribbon tab that is displayed only when a particular type of object, such as a hatch or table, is included in a selection. Toolbars can be changed to contextual tabs in the CUI.
A type of linear dimension that uses the second extension line origin of a selected dimension as its first extension line origin, breaking one long dimension into shorter segments that add up to the total measurement. Also called chain dimension. (DIMCONTINUE)
A series of point locations used as a mechanism to control the shape of a B-spline. These points are connected by a series of line segments for visual clarity and to distinguish the control frame from fit points. The SPLFRAME system variable must be turned on to display control frames.
See control frame.
In 3D surface meshes, the bicubic surface (one curved in the M direction and another in the N direction) interpolated between four edges.
Functions that extract individual X, Y, and Z coordinate values from different points to create a new, composite point. Also called X,Y,Z point filters.
A sharpened ridge that defines one or more edges of a mesh face subobject. (MESHCREASE)
Generally, curves or lines that define the profile (shape) of a lofted solid or surface. Cross sections can be open or closed. A lofted solid or surface is drawn in the space between the cross sections. (LOFT)
A type of cursor consisting of two lines that intersect.
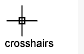
A rectangular area drawn to select objects fully or partly within its borders.
SA color-dependent plot style table.
Method for cycling between different behaviors while editing geometry, either in a command or when grip-editing. Pressing and releasing the CTRL key cycles the behavior. For constrained geometry, CTRL-cycling switches between enforcing and relaxing constraints.
A drawing file that is open in the program, and receives any command or action that you enter.
See pointer and crosshairs.
See shortcut menu.
In a dynamic block reference, used to manipulate the geometry and custom properties.
A type of object that is created by an ObjectARX application and that typically has more specialized capabilities than standard objects. Custom objects include parametric solids (AutoCAD Mechanical Desktop), intelligently interactive door symbols (AutoCAD Architecture), polygon objects (AutoCAD Map 3D), and associative dimension objects (AutoCAD and AutoCAD LT). See also proxy object and object enabler.
An XML-based file that stores customization data. You modify a customization file through the Customize User Interface dialog box. CUI files replace MNU, MNS, and MNC files that were used to define menus in earlier releases.
A connection between a table and an external source of data.
A notation for specifying latitude and longitude. For example, 35.1234°, 100.5678°.
Latitude always precedes longitude
See initial environment.
The lighting in a shaded viewport when the sun and user lights are turned off. Faces are lighted by two distant light sources that follow the viewpoint as you move around the model.
The value that is accepted when you press ENTER at a sub-prompt. The default value is displayed in angle brackets <>. See also default.
Points for creating a dimension. The program refers to the points to modify the appearance and value of a nonassociative dimension when the dimensioned object is modified. Also called defpoints and stored on the special layer DEFPOINTS.
The nongraphical data area of a drawing file that stores block definitions.
In a dynamic block definition, how associated objects are displayed when you select a parameter, grip, or action.
Named objects brought into a drawing by an external reference. See also named object and symbol table.
See dependent named objects (in xrefs).
See underlay.
For Direct Interpretively Evaluated String Expression Language. A macro language for altering the status line with the MODEMACRO system variable and for customizing menu items.
An object's predominant color.
An arc (usually with arrows at each end) spanning the angle formed by the extension lines of an angle being measured. The dimension text near this arc sometimes divides it into two arcs. See also angular dimension.
A named group of dimension settings that determines the appearance of the dimension and simplifies the setting of dimension system variables. (DIMSTYLE)
The measurement value of dimensioned objects.
A set of numeric values, text strings, and settings that control dimensioning features. (DIMSTYLE)
Parametric dimensions that control the size, angle, or position of geometry relative to the drawing or other objects.When dimensions are changed, the object resizes.
A method to specify a second point by first moving the cursor to indicate direction and then entering a distance.
Combining color dots to give the impression of displaying more colors than are actually available.
A user interface element that can be either docked, anchored, or floating in the drawing area. Dockable windows include the command window, tool palettes, Properties Palette, and so on.
The area in which your drawings are displayed and modified. The size of the drawing area varies, depending on the size of the AutoCAD window and on how many toolbars and other elements are displayed. See also AutoCAD window.
The smallest rectangle that contains all objects in a drawing, positioned on the screen to display the largest possible view of all objects. (ZOOM)
See grid limits.
A collection of drawings assembled using the Publish dialog box.
A collection of known settings that define the behavioral properties of the drawing environment and/or drawing at a known period of time, such as when an action macro was recorded or before the playback of an action macro.
A drawing file with preestablished settings for new drawings such as acad.dwtand acadiso.dwt however, any drawing can be used as a template. See also initial environment.
A non-parametric dimension enclosed in parentheses that shows the current value of geometry. The value is updated when the geometry changes size, but it does not control geometry.
A parametric dimension that determines the size of geometry and resizes the object when its value changes.
A lookup property is considered invertible when a manual change in the lookup value for a block reference causes other properties values change.
For drawing set descriptions. A file format for saving a description of a drawing set that has been assembled using the Publish dialog box.
For sheet set data. The XML file format used to store the associations and information that define a sheet set.
An open, published, and secure file format developed by Autodesk, DWF enables you to combine and publish rich 2D- and 3D-design data and share it with others.
See underlay.
A version of DWF based on the XML Paper Specification (XPS) from Microsoft. DWFx enables DWF files to be viewed using the free Microsoft XPS Viewer. Generically referred to as DWF.
Standard file format for saving vector graphics. See also DWF and DXF.
For drawing interchange format. An ASCII or binary file format of a drawing file for exporting drawings to other applications or for importing drawings from other applications. See also DWF and DWG.
Dimensional constraint (Constraint Form property = "dynamic") that displays the constraints only when you select the constrained object.
See also: parameter constraint
See also: annotational constraint
Temporary dimensions that appear on objects, including dynamic block references, when they are grip edited.
The boundary of a face.
Effects such as overhang and jitter that control how edges are displayed in a shaded model.
The digital equivalent of a set of plotted drawings. You create an electronic drawing set by publishing drawings to a DWF file.
The default Z value above or below the XY plane of the current user coordinate system, which is used for entering coordinates and digitizing locations. (ELEV)
To use object linking and embedding (OLE) information from a source document in a destination document. An embedded object is a copy of the information from a source document that is placed in the destination document and has no link to the source document. See also link.
A selection set that contains no objects.
A CUI file that is typically controlled by a CAD manager. It is often accessed by many users and is stored in a shared network location. The file is read-only to users to prevent the data in the file from being changed. A CAD manager creates an enterprise CUI file by modifying a main CUI file and then saving the file to the support location defined in the Options dialog box, Files tab.
A bitmap that is used to simulate reflections in materials that have reflective properties. The map is “wrapped” around the scene and any reflective object will show the appropriate portion of the map in the reflective parts of its material.
A setting stored in the operating system that controls the operation of a program.
An area on the ribbon associated with a ribbon panel. An expanded panel contains additional tools and controls. See also ribbon panel and ribbon.
To disassemble a complex object, such as a block, dimension, solid, or polyline, into simpler objects. In the case of a block, the block definition is unchanged. The block reference is replaced by the components of the block. See also block, block definition, and block reference. (EXPLODE)
Independent objects that have the appearance of a dimension but are not associated with the dimensioned object or each other. Controlled by the DIMASSOC system variable. See also associative dimension, nonassociative dimension, and explode. (EXPLODE)
When hovered over the tooltip for a period of time, displays additional information.
See drawing extents.
A drawing file referenced by another drawing. (XREF)
A 3D solid created by sweeping an object that encloses an area along a linear path.
A triangular or quadrilateral portion of a surface object.
A setting in the visual style that controls how color is displayed on a face.
A setting in the visual style that defines the shading on a face.
The underlying structure of the face of a 3D solid, surface, or mesh. Facets can be quadrilateral or triangular. Smoothing a mesh object increases the number of facets for each face.
The tolerance that applies to specific features or patterns of features. Feature control frames always contain at least a geometric characteristic symbol to indicate the type of control and a tolerance value to indicate the amount of acceptable variation.
A multisegmented line specified to select objects it passes through.
A specialized text object set up to display data that may change during the life cycle of the drawing. When the field is updated, the latest value of the field is displayed. (FIELD)
A solid color covering an area bounded by lines or curves. (FILL)
See coordinate filters.
Final gathering is an optional, additional step to calculating global illumination. Using a photon map to calculate global illumination can cause rendering artifacts such as dark corners and low-frequency variations in the lighting. You can reduce or eliminate these artifacts by turning on final gathering, which increases the number of rays used to calculate global illumination.
Final gathering can greatly increase rendering time. It is most useful for scenes with overall diffuse lighting, less useful for scenes with bright spots of indirect illumination.
You turn on final gathering on the Advanced Render Settings palette. See also global illumination.
The interactive graphical tooltip that is displayed when the SteeringWheel is pinned during startup.
Locations that a B-spline must pass through exactly or within a fit tolerance. See also interpolation points and approximation points.
The setting for the maximum distance that a B-spline can pass for each of the fit points that define it.
A ribbon panel that is not attached to the rest of the ribbon or application frame.
See layout viewports.
A character set, made up of letters, numbers, punctuation marks, and symbols of a distinctive proportion and design.
The American unit of illuminance (symbol: fc). Lm/ft^2.
The American unit of illuminance (symbol: fc). Lm/ft^2
An individual, static image in an animated sequence. See also motion path.
A setting that suppresses the display of objects on selected layers. Objects on frozen layers are not displayed, regenerated, or plotted. Freezing layers shortens regenerating time. See also thaw. (LAYER)
Faces with their normals pointed outward.
Properties that are common between a selection of objects. These include Color, Layer, Linetype, Linetype scale, Plot style, Lineweight, Hyperlink, and Thickness.
The relative height along the specified up-direction defined for a geographic marker.
Visual representation of geographic location information.
Rules that define the geometric relationships of objects (or points of objects) elements and control how an object can change shape or size.
Geometric constraints are coincident, collinear, concentric, equal, fix, horizontal, parallel, perpendicular, tangent, and vertical.
All graphical objects such as lines, circles, arcs, polylines, and dimensions. Nongraphical objects, such as linetypes, lineweights, text styles, and layers are not considered geometry. See also named object.
A tool that permits you to manipulate a 3D object uniformly or along a specified axis or plane. Examples of gizmos include the 3D Move, 3D Rotate, and 3D Scale gizmos. They are displayed when you select a 3D object.
An indirect illumination technique that allows for effects such as color bleeding. As light hits a colored object in the model, photons bounce to adjacent objects and tint them with the color of the original object.
A type of shading that uses a transition from cool to warm colors rather than from dark to light.
See drawing area.
See AutoCAD window and drawing area.
An area covered with regularly spaced dots or lines to aid drawing. The grid spacing is adjustable. The grid dots are never plotted. See also grid limits. (GRID)
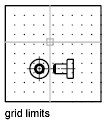
The user-defined rectangular boundary of the drawing area covered by dots when the grid is turned on. Also called drawing limits. (LIMITS)
The editing capabilities activated when grips are displayed on an object: stretching, moving, rotating, scaling, and mirroring.
An icon that you use in a 3D view to easily constrain the movement or rotation of a selection set of objects to an axis or a plane. (3DMOVE, 3DROTATE)
Small squares and triangles that appear on objects you select. After selecting the grip, you edit the object by dragging it with the pointing device instead of entering commands.
The XY plane of the user coordinate system when perspective projection is turned on. The ground plane displays with a color gradient between the ground horizon (nearest to the horizon) and the ground origin (opposite the horizon). See also sky and underground.
Lines or curves that intersect each cross section of a lofted solid or surface and that define the form by adding additional wireframe information to the object. (LOFT)
A unique alphanumeric tag for an object in the program's database.
For Heidi Device Interface. An interface for developing device drivers that are required for peripherals to work with the program and other Autodesk products.
The process of transparently displaying user interface elements on top of or over the drawing area without obscuring the view of the objects drawn on the drawing area.
An open 2D or 3D spiral. (HELIX)
The legacy way to access online Help. In the current version of AutoCAD, you can find Help on the InfoCenter toolbar or by pressing F1.
For hue, lightness, and saturation. A system of defining color by specifying the amount of hue, lightness, and saturation.
A special view saved with the drawing that is controlled through the ViewCube tool. The Home view is similar in concept to the default, initial view presented when a drawing is first opened.
An optional line segment connecting the tail of a leader line with the leader content.
The ribbon, when it is oriented across the top of the file window.
A method by which a drawing file can be dragged from a Web page and inserted into another drawing.
For Initial Graphics Exchange Specification. A standard format for digital representation and exchange of information between CAD/CAM systems. In AutoCAD-based products, the commands to import and export IGES files are available only in AutoCAD Mechanical.
In photometry, illuminance is the total luminous flux incident on a surface per unit area.
Scales the effect of the base material’s bump mapping in areas lit by indirect light.
Illumination techniques such as global illumination and final gathering, that enhance the realism of a scene by simulating radiosity, or the interreflection of light between objects in a scene.
The variables and settings for new drawings as defined by the default drawing template, such as acad.dwg or acadiso.dwg. See also template drawing.
In a dynamic block definition, a parameter property other than that of a lookup, alignment, or base point parameter that you can add as a column to a lookup table. When the parameter values in a dynamic block reference match a row of input property values, the corresponding lookup property values in that table row are assigned to the block reference. (BLOOKUPTABLE)
A user interface object that can be customized, such as a toolbar, pull-down menu, shortcut key, dockable window, and so on.
Defining points that a B-spline passes through. See also approximation points and fit points.
An enclosed area within another enclosed area. Islands may be detected as part of the process of creating hatches, polylines, and regions. (BHATCH, BOUNDARY)
For International Standards Organization. The organization that sets international standards in all fields except electrical and electronics. Headquarters are in Geneva, Switzerland.
A drafting option that aligns the cursor with two of three isometric axes and displays grid, making 2D isometric drawings easier to create.
In a dynamic block definition, the point on a parameter that drives its associated action when edited in the block reference.
A block used to label views and details. Labels contain data, such as a title, view number, and scale, that is associated with the referenced view. See also callout block.
The portion of a leader object that acts as a pointer to the object being called out. A landing can either be a straight line or a spline curve.
An optional space between a leader tail and the leader content.
A logical grouping of data that are like transparent acetate overlays on a drawing. You can view layers individually or in combination. (LAYER)
A list showing the objects on each layer. A layer index is used to locate what portion of the drawing is read when you partially open a drawing. Saving a layer index with a drawing also enhances performance when you work with external references. The INDEXCTL system variable controls whether layer and spatial indexes are saved with a drawing.
Assignments of a set of layers to another set of layers that defines standards. These standards include layer names and layer properties. Also called layer mappings.
The environment in which you create and design paper space layout viewports to be plotted. Multiple layouts can be created for each drawing.
Objects that are created in paper space that display views. See also paper space. (VPORTS)
The portion of a leader line that is connected to the annotation.
Defines the magnification properties of a camera's lens. The greater the lens length, the narrower the field of view.
The property assigned to a mesh object to control how much the edges of the object are smoothed. Level 0 (zero) represents the least rounded shape for a specified mesh object. Higher levels result in increased smoothness.
The graphic representation of a point light or a spotlight.
See drawing limits.
See linetype.
How a line or type of curve is displayed. For example, a continuous line has a different linetype than a dashed line. Also called line font. (LINETYPE)
A width value that can be assigned to all graphical objects except TrueType® fonts and raster images.
To use object linking and embedding (OLE) to reference data in another file. When data is linked, any changes to it in the source document are automatically updated in any destination document. See also embed.
Common latitude longitudinal-based coordinate system where latitude and longitude are both measured from -90 to 90 degrees.
Longitude begins at 0 degrees at the Prime Meridian in Greenwich, England and is measured from -180 to 180.
Latitude is 0 degrees at the equator and is measured from -90 to 90.
A solid or surface that is drawn through a set of two or more cross-section curves. The cross sections define the profile (shape) of the resulting solid or surface. Cross sections (generally, curves or lines) can be open or closed. (LOFT)
In a dynamic block definition, a lookup parameter that you add to a lookup table. The lookup parameter label is used as the property name. When the parameter values in a dynamic block reference match a row of input property values, the corresponding lookup property values in that table row are assigned to the block reference. (BLOOKUPTABLE)
Defines properties for and assigns property values to a dynamic block. Assigns property values to the dynamic block reference based on how the block is manipulated in a drawing. (BLOOKUPTABLE)
The SI unit of luminous flux (Symbol: lm). Cd * Sr
This refers to the aggregation of a lamp or lamps and its fixture. The fixture may be a simple can or a complex armature with constrained joints.
Luminance is the value of light reflected off a surface. It is a measure of how bright or dark we perceive the surface.
The perceived power in per unit of solid angle. The total luminous flux for a lamp is the perceived power emitted in all directions.
The SI unit of illuminance (symbol: lx). Lm/m^2
A selection set of all the objects that have been created during the playback of an action macro up to the command that is requesting a selection set.
A writable CUI file that defines most of the user interface elements (including the standard menus, toolbars, keyboard accelerators, and so on). The acad.cui file (the default main CUI file) is automatically loaded when you start AutoCAD.
A single comment or a redline geometry correction inserted into a DWF file using Autodesk Design Review.
A group of markups contained within a single DWF file.
In tables, an adjacent cell selection that has been combined into a single cell.
A tessellated, or subdivided object type that is defined by faces, edges, and vertices. Mesh can be smoothed to achieve a more rounded appearance and creased to introduce ridges. Before AutoCAD 2010, only the less modifiable polygon and polyface mesh was available.
The small version of SteeringWheels. No labels are displayed on any of the wedges and they are often the size of the cursor.
To create a new version of an existing object by reflecting it symmetrically with respect to a prescribed line or plane. (MIRROR)
A software setting or operating state.
A two- or three-dimensional representation of an object.
One of the two primary spaces in which objects reside. Typically, a geometric model is placed in a three-dimensional coordinate space called model space. A final layout of specific views and annotations of this model is placed in paper space. See also paper space. (MSPACE)
A type of display that splits the drawing area into one or more adjacent rectangular viewing areas. See also layout viewports, TILEMODE, and viewport. (VPORTS)
Defines the path or target of a camera. A path can be a line, arc, elliptical arc, circle, polyline, 3D polyline, or spline.
A DWF file that contains multiple sheets.
A leader object that creates annotations with multiple leader lines.
Describes the various types of nongraphical information, such as styles and definitions, stored with a drawing. Named objects include linetypes, layers, dimension styles, text styles, block definitions, layouts, views, and viewport configurations. Named objects are stored in definition (symbol) tables.
See dependent named objects (in xrefs).
A saved motion path object that is linked to a camera or target.
A tool in Microsoft Excel that provides a method to assign a meaningful name to a single cell or a range of cells.
A view saved for restoration later. (VIEW)
An object snap specification to locate points, dimension definition points, and dimension text origins.
A dimension that does not automatically change as the associated geometry is modified. Controlled by the DIMASSOC system variable. See also associative dimension and exploded dimension.
A normal is a vector that defines which way a face is pointing. The direction of the normal indicates the front, or outer surface of the face.
Selecting an object first and then performing an operation on it rather than entering a command first and then selecting the object.
For nonuniform rational B-spline curve. A B-spline curve or surface defined by a series of weighted control points and one or more knot vectors. See also B-spline curve.
One or more graphical elements, such as text, dimensions, lines, circles, or polylines, treated as a single element for creation, manipulation, and modification. Formerly called entity.
A tool that provides specific viewing and standard editing access to a custom object when the ObjectARX application that created the custom object is not present. See also custom object and proxy object.
Methods for selecting commonly needed points on an object while you create or edit a drawing. See also running object snap and object snap override.
Turning off or changing a running Object Snap mode for input of a single point. See also Object Snap mode and running object snap.
A compiled-language programming environment for developing AutoCAD applications.
For object linking and embedding. An information-sharing method in which data from a source document can be linked to or embedded in a destination document. Selecting the data in the destination document opens the source application so that the data can be edited. See also embed and link.
Projection of opaque and transparent areas onto objects, creating the effect of a solid surface with holes or gaps.
The point where coordinate axes intersect. For example, the origin of a Cartesian coordinate system is where the X, Y, and Z axes meet at 0,0,0.
A setting that limits pointing device input to horizontal or vertical (relative to the current snap angle and the user coordinate system). See also snap angle and user coordinate system (UCS).
Having perpendicular slopes or tangents at the point of intersection.
A lookup property whose value is determined by input properties (other parameter properties) through the use of a lookup table.
A collection of plot device and other settings that affect the appearance and format of the final output. These settings can be modified and applied to other layouts.
To shift the view of a drawing without changing magnification. See also zoom. (PAN)
One of two primary spaces in which objects reside. Paper space is used for creating a finished layout for printing or plotting, as opposed to doing drafting or design work. You design your model using the Model tab. See also model space and viewport. (PSPACE)
In a dynamic block definition, defines custom properties for the dynamic block by specifying positions, distances, and angles for geometry in the block.
A tool on the Parameter Sets tab of the Block Authoring Palettes window that adds one or more parameters and one or more associated actions to the dynamic block definition.
Ability to establish relationships between objects, to drive the size and orientation of geometry with model and user-defined parameters.
Feature in AutoCAD that assigns constraints to objects, establishing the distance, location, and orientation of objects with respect to other objects.
Any CUI file that is not defined as the main CUI file. You can load and unload partial CUI files as you need them during a drawing session.
Defines the direction and length that a profile curve is lofted, swept, or extruded to create a solid or surface. (SWEEP, LOFT, EXTRUDE)
Complete plotter configuration file. PC2 files contain all plot settings and device-specific settings that were saved in previous versions. See also PCP file and PC3 file.
Partial plotter configuration file. PC3 files contain plot settings information such as the device driver and model, the output port to which the device is connected, and various device-specific settings, but do not include any custom plotter calibration or custom paper size information. See also PMP file, STB file, and CTB file.
Partial plotter configuration file. PCP files contain basic plot specifications and pen parameters that were saved in previous versions. Plot settings that are stored in a PCP file include pen assignments, plotting units, paper size, plot rotation, plot origin, scale factor, and pen optimization level. See also PC2 file and PC3 file.
A method of optimizing 3D graphics performance. The performance tuner examines your graphics card and 3D display driver and decides whether to use software or hardware implementation for features that support both.
Customizes the executable file during installation with the user name, company, and other information.
Objects in 3D seen by an observer positioned at the viewpoint looking at the view center. Objects appear smaller when the distance from the observer (at the view point) to the view center increases. Although a perspective view appears realistic, it does not preserve the shapes of objects. Parallel lines seemingly converge in the view. The program has perspective view settings for VPORTS table entries as well as viewport objects.
Photometric lights are physically-correct lights. Physically correct lights attenuate as the square of the distance. Photometry is the science of measurement of visible light in terms of its perceived brightness.
A technique to generate the indirect illumination effects of global illumination used by the renderer. When it calculates indirect illumination, the renderer traces photons emitted from a light. The photon is traced through the model, being reflected or transmitted by objects, until it strikes a diffuse surface. When it strikes a surface, the photon is stored in the photon map.
Rendering that resembles a photograph.
The button on a pointing device that is used to select objects or specify points on the screen. For example, on a two-button mouse, it is the left button by default.
Clicking and acquiring a point on an object in the drawing.
The selection of objects before an action macro or command is issued.
A selection set of objects that are selected prior to the execution of an action macro or a command. See also pre-selection set.
A view orientation from a point on the positive Z axis toward the origin (0,0,0). (PLAN)
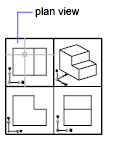
A flat face that can be located anywhere in 3D space.
Mapping of objects or images onto a plane.
A flat surface that can be located anywhere in 3D space. (PLANESURF)
The process of executing the actions stored in a previously recorded action macro.
See polyline.
An object property that specifies a set of overrides for color, dithering, gray scale, pen assignments, screening, linetype, lineweight, endstyles, joinstyles, and fill styles. Plot styles are applied at plot time.
A set of plot styles. Plot styles are defined in plot style tables and apply to objects only when the plot style table is attached to a layout or viewport.
Plug-ins are libraries of reuseable content that extend the functionality of AutoCAD. Plug-ins are created by third party developers and can be accessed from the Featured Technologies and Content channel of the Communications Center.
Plot Model Parameter. File containing custom plotter calibration and custom paper size information associated with plotter configuration file.
1. A location in three-dimensional space specified by X, Y, and Z coordinate values. 2. An object consisting of a single coordinate location. (POINT)
See coordinate filters.
A cursor on a video display screen that can be moved around to place textual or graphical information. See also crosshairs.
Objects copied around a specified center point a specified number of times. (ARRAY)
A precision drawing tool used to snap to incremental distances along the polar tracking alignment path. See also polar tracking.
A precision drawing tool that displays temporary alignment paths defined by user-specified polar angles. See also Polar Snap.
Legacy mesh types that were available before AutoCAD 2010. Although you can continue to create polygonal and polyface mesh (for example, by setting MESHTYPE to 0), the newer, more modifiable mesh type is recommended.
A multisided area specified to select objects in groups. See also crossing selection and window selection.
An object composed of one or more connected line segments or circular arcs treated as a single object. Also called pline. (PLINE, PEDIT)
A swept solid that is drawn the same way you draw a polyline or that is based on an existing line. By default, a polysolid always has a rectangular profile. You can specify the height and width of the profile. (POLYSOLID)
The drawing state prior to the playback of an action macro.
A selection set of objects that is defined prior to the execution of an action macro.
The fragment of a broken table that contains the beginning set of rows up to the first table break.
Basic 3D forms such as boxes, cones, cylinders, pyramids, wedges, spheres, and tori. You can create primitive meshes and primitive 3D solid objects.
Materials that generate a 3D pattern in two or more colors, and apply it to an object. These include marble and wood. Also called template materials.
An object that is swept, extruded, or revolved and defines the shape of the resulting solid or surface. (SWEEP, EXTRUDE, REVOLVE)
A message on the command line or in a tooltip that asks for information or requests action such as specifying a point.
A substitute for a custom object when the ObjectARX application that created the custom object is not available. See also custom object and object enabler.
A push pin-shaped button used on the ribbon and in the application menu. On the ribbon, push pins are used to keep a ribbon panel expanded. In the application menu, push pins keep an item in the list of recently opened items.
A template file format used to publish drawings to the Web.
A thumbnail image of a drawing, layout or model space that is displayed using Quick View tools.
A tool to preview and switch between open drawings and layouts in a drawing.
The renderer can generate reflections and refractions. Ray tracing traces the path of rays sampled from the light source. Reflections and refractions generated this way are physically accurate.
You turn on ray tracing on the Advanced Render Settings palette.
A way that the renderer can generate shadows. Ray tracing traces the path of rays sampled from the light source. Shadows appear where rays have been blocked by objects. Ray-traced shadows have sharp edges.
Ray-traced shadows are active when Shadow Map is turned off on the Advanced Render Settings palette.
The input captured during the recording of an action macro for a sub-prompt of a command.
To break a table into multiple parts that are evenly spaced and set at a user-specified height using the table breaking grips.
To quickly refresh or clean up blip marks in the current viewport without updating the drawing's database. See also regenerate. (REDRAW)
A definition, known as an external reference or block reference, that is used and stored in the drawing. See also block (BLOCK) and external reference (xref). (XREF)
To quadruple the number of faces in a mesh object as you reset the baseline level of smoothness. (You cannot make a mesh courser than its baseline level.) You can also refine specified mesh faces without resetting the baseline level of smoothness for the object. (MESHREFINE)
Increases or decreases the amount of energy the material reflects.
The color of a highlight on shiny material. Also called specular color.
In a dynamic block reference, the axis about which a flip action's selection set flips when the associated parameter is edited through a grip or the Properties palette.
Creates the effect of a scene reflected on the surface of a shiny object.
How light distorts through an object.
To update a drawing's screen display by recomputing the screen coordinates from the database. See also redraw. (REGEN)
Two-dimensional enclosed areas that have physical properties such as centroids or centers of mass. You can create regions from objects that form closed loops. They area commonly created in order to apply hatching and shading. (REGION)
Coordinates specified in relation to previous coordinates.
Ability to temporarily ignore constraints while editing geometry. After the geometry is edited, the constraints are either removed or retained based on whether the constraint is still valid for the edited geometry.
An item that is assigned to an action node that pauses the playback of an action macro so a user can provide some form of input before playback resumes.
Adds a lookup grip to a dynamic block reference. When you click this grip, a drop-down list of the lookup values for that lookup property (column in the lookup table) is displayed. When you select a value from the list, the corresponding input property values are assigned to the block reference. Depending on how the block was defined, this usually results in a change in the block reference's geometry. (BLOOKUPTABLE)
Restores the previous view or movement path created by the Autodesk® ViewCube® navigation tool, SteeringWheels, and other navigation tools.
For red, green, and blue. A system of defining colors by specifying percentages of red, green, and blue.
A palette that displays buttons and controls used for both 2D drawing and annotation and 3D modeling, viewing, and rendering. See also ribbon tab and ribbon panel and slide-out panel. (RIBBON)
A labeled control in the ribbon. Ribbon panels contain buttons or other controls. Multiple ribbon panels make a ribbon tab.
The most general control on the ribbon. Ribbon tabs contain ribbon panels, which contain buttons or other controls.
Curved arrows located above the ViewCube tool with which you can rotate the current view 90 degrees clockwise or counterclockwise.
Value to simulate how light hitting a face is reflected back to the user. A high roughness value simulates a non-shiny or rough object (sandpaper/carpet). A low roughness value simulates a very shiny object (metals, some plastics.)
A horizontally adjacent table cell selection spanning the width of the table. A single row is one cell in height.
Information published by a website to which you subscribe. Usually allows users to receive notifications when new content (articles) are posted. RSS stands for Rich Site Summary (or Really Simple Syndication).
A line that stretches dynamically on the screen with the movement of the cursor. One endpoint of the line is attached to a point in your drawing, and the other is attached to the moving cursor.
Setting an Object Snap mode so it continues for subsequent selections. See also Object Snap mode and object snap override. (OSNAP)
Sampling is an antialiasing technique. It provides a "best guess" color for each rendered pixel. The renderer first samples the scene color at locations within the pixel or along the pixel's edge, then uses a filter to combine the samples into a single pixel color.
To update the objects in the original reference (external or block reference) with changes made to objects in a working set during in-place reference editing.
The display of an annotative object based on the annotation scales that the object supports. For example, if an annotative object supports two annotations scales, it has two scale representations
A set of commands executed sequentially with a single SCRIPT command. Script files are created outside the program using a text editor, saved in text format, and stored in an external file with the file extension .scr.
A user-defined keyword used to search for commands in the menu browser.
Any fragment of a broken table that does not contain the beginning set of rows.
A specific type of action tree node that is used to handle selection activities.
The ability to define the pivot point for reorienting a model based on the current selection.
One or more selected objects that a command can act upon at the same time.
In a dynamic block definition, the geometry associated with an action.
A shadow map is a bitmap that the renderer generates during a pre-rendering pass of the scene. Shadow maps don't show the color cast by transparent or translucent objects. On the other hand, shadow maps can have soft-edged shadows, which ray-traced shadows cannot.
Shadow mapped shadows provide softer edges and can require less calculation time than ray-traced shadows, but are less accurate. On the Advanced Render Settings palette, shadow mapped shadows are active when Shadow Map is turned on.
ShapeManager is the Autodesk technology that provides 3D solid modeling to AutoCAD and other products.
A layout selected from a drawing file and assigned to a sheet set. See also sheet set.
A table listing all sheets in a sheet set. A sheet list table can be generated automatically with the Sheet Set Manager.
A named selection of sheets in a sheet set that can be conveniently recalled for archiving, transmitting, and publishing operations.
An organized and named collection of sheets from several drawing files. See also sheet. (SHEETSET)
Keys and key combinations that start commands; for example, CTRL+S saves a file. The function keys (F1, F2, and so on) are also shortcut keys. Also known as accelerator keys.
The menu displayed at your cursor location when you right-click your pointing device. The shortcut menu and the options it provides depend on the pointer location and other conditions, such as whether an object is selected or a command is in progress.
A saved view that can later be restored by name or with ShowMotion. A shot can contain a static thumbnail of the saved view or camera motion that can be played back as an animation.
User interface element where you can access named views (shots) that are stored in the current drawing. The named views (shots) are organized by sequences and can contain movements.
The background color of the drawing area when perspective projection is turned on. The sky displays with a color gradient between the sky horizon (nearest to the horizon) and the sky zenith (opposite the horizon). See also ground plane.
A file that contains a raster image or snapshot of the objects displayed in the drawing area. Slide files have the file extension .sld. (MSLIDE, VSLIDE)
A collection of slide files organized for convenient retrieval and display. Slide library names have the extension .slb and are created with the slidelib.exe utility.
An area on the ribbon associated with a ribbon panel. A slide-out panel contains additional tools and controls. See also ribbon panel and ribbon.
Smoothing of the edges between polygon faces.
A property of mesh objects that controls the roundness of the object. Objects with higher levels of smoothness have more faces, or tessellations.
The angle that the snap grid is rotated.
The invisible grid that locks the pointer into alignment with the grid points according to the spacing set by Snap. Snap grid does not necessarily correspond to the visible grid, which is controlled separately by GRID. (SNAP)
A mode for locking a pointing device into alignment with an invisible rectangular grid. When Snap mode is on, the screen crosshairs and all input coordinates are snapped to the nearest point on the grid. The snap resolution defines the spacing of this grid. See also Object Snap mode. (SNAP)
The spacing between points of the snap grid.
A property of a solid that allows you to see and modify the original forms of the solid.
An object that represents the entire volume of an object, for example a box.
A basic solid form. Solid primitives include: box, wedge, cone, cylinder, sphere, torus, and pyramid.
A list that organizes objects based on their location in space. A spatial index is used to locate what portion of the drawing is read when you partially open a drawing. Saving a spatial index with a drawing also enhances performance when working with external references. The INDEXCTL system variable controls whether layer and spatial indexes are saved with a drawing.
The light in a narrow cone where the angle of the incoming beam equals the angle of the reflected beam.
A mesh face that has been subdivided along a specified vector.
For plot style table file. Contains plot styles and their characteristics.
Tool set that provides access to 2D and 3D navigation tools.
In a dynamic block definition that contains a stretch action or a polar stretch action, determines how the objects within or crossed by the frame are edited in the block reference.
A command prompt that instructs for a form of input to complete a command or alter a property.
A division, or tessellation in a mesh object. As a mesh object is smoothed, the number of subdivisions increases.
Any part of a solid: a face, an edge, or a vertex. Also, an original individual form that is part of a composite solid.
Subscription members can access the latest releases of Autodesk software, incremental product enhancements, personalized web support, and self-paced e-Learning in InfoCenter. To access Subscription Center, go to the InfoCenter toolbar and click the Key button.
A named collection of sheets in a sheet set that is often organized by discipline or workflow stage. See also view category.
An open-ended, infinitely thin object that corresponds to the shape of a 3D object. You can create surfaces in several ways. For example, you can convert from other objects such as mesh, or with sweep, loft, or revolve operations that create open-ended objects.
Positive direction perpendicular to the surface of an object.
A solid or surface created in the shape of the specified profile (the swept object) swept along the specified path. (SWEEP)
A representation of an item commonly used in drawings. Symbols are inserted in drawings as blocks.
A collection of block definitions stored in a single drawing file.
See definition table and block definition table.
A name that is recognized as a mode, size, or limit. Read-only system variables, such as DWGNAME, cannot be modified directly by the user.
A rectangular array of cells that contain annotation, primarily text but also blocks. In the AEC industry, tables are often referred to as “schedules” and contain information about the materials needed for the construction of the building being designed. In the manufacturing industry, they are often referred to as “BOM” (bills of materials). (TABLE)
The point at the bottom of a table row where the table will be split into a supplementary table fragment.
A style that contains a specific table format and structure. A table style contains at least 3 cell styles.
Data files created during an program session. The files are deleted by the time you end the session. If the session ends abnormally, such as during a power outage, temporary files might be left on the disk.
Lines that help you visualize a curved surface.
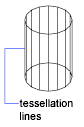
In a 3D mesh object, tessellations indicate the boundaries of the mesh faces.
A named, saved collection of settings that determines the appearance of text characters—for example, stretched, compressed, oblique, mirrored, or set in a vertical column.
The projection of an image (such as a tile pattern) onto an object (such as a chair).
A setting that displays previously frozen layers. See also freeze. (LAYER)
The distance certain objects are extruded to give them a 3D appearance. (PROPERTIES, CHPROP, ELEV, THICKNESS)
See model viewports.
A system variable that controls whether viewports can be created as movable, resizable objects (layout viewports), or as nonoverlapping display elements that appear side-by-side (model viewports). See also viewport.
A small instructional message that appears over the drawing window and is specific to the active navigation tool from a SteeringWheel.
Part of the interface containing icons that represent commands.
A small box of text that identifies or explains an object or interface element when the cursor hovers near or over it.
A way to locate a point relative to other points on the drawing.
A cluster of buttons that follows the cursor as you move it over the window.
How light is scattered through an object.
Increases or decreases the amount of energy a transparent material transmits out to the scene.
A quantity defining how much light is let through an object.
A command started while another is in progress. Precede transparent commands with an apostrophe.
The positive and negative normal of the material will be considered during the rendering process.
See user coordinate system (UCS).
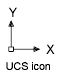
An icon that indicates the orientation of the UCS axes. (UCSICON)
Objects with unsolved degrees of freedom are underconstrained.
The XY plane of the user coordinate system when perspective projection is turned on and when viewed from below ground. The underground plane displays with a color gradient between the earth horizon (nearest to the horizon) and the earth azimuth (opposite the horizon). See also ground plane and sky.
A DWF, or DGN file used to provide visual context in a drawing file. Underlays cannot be edited, and do not provide the full range of notification. Underlays cannot be bound to a drawing. See also external reference (xref).
A vector defining what direction is Up. By default this is the positive Z – axis (0,0,+1).
The up direction and the north direction are always constrained such that they are perpendicular to each other.
A user-defined coordinate system that defines the orientation of the X, Y, and Z axes in 3D space. The UCS determines the default placement of geometry in a drawing. See also world coordinate system (WCS).
Named user-defined variable (real number or an expression) that can be used in expressions for dimensional constraints or other user parameters.
The material’s coordinate space. Used instead of XYZ because that is usually reserved for the world coordinate system (WCS). Most material maps are a 2D plane assigned to a 3D surface. The U, V, and W coordinates parallel the relative directions of X, Y, and Z coordinates. If you look at a 2D map image, U is the equivalent of X, and represents the horizontal direction of the map. V is the equivalent of Y, and represents the vertical direction of the map. W is the equivalent of Z and represents a direction perpendicular to the UV plane of the map.
A specific type of action node that is used to handle requests for user input and hold the recorded value that was captured during the recording of an action macro.
In a dynamic block definition, a range or list of values specified for a linear, polar, XY, or rotation parameter.
A mathematical object with precise direction and length but without specific location.
A location where edges or polyline segments meet.
The ribbon when it is oriented vertically, usually on the left or right of the file window.
A graphical representation of a model from a specific location (viewpoint) in space. See also viewpoint and viewport. (3DORBIT, VPOINT, DVIEW, VIEW)
A named collection of views in a sheet set that is often organized by function. See also subset.
User interface element that displays the current orientation of a model, and allows you to interactively rotate the current view or restore a preset view.
The location in 3D model space from which you are viewing a model. See also view and viewport. (3DORBIT, DVIEW, VPOINT)
A bounded area that displays some portion of the model space of a drawing. The TILEMODE system variable determines the type of viewport created. 1. When TILEMODE is off (0), viewports are objects that can be moved and resized on a layout. (MVIEW) 2. When TILEMODE is on (1), the entire drawing area is divided into nonoverlapping model viewports. See also TILEMODE, view, and viewpoint. (VPORTS)
A named collection of model viewports that can be saved and restored. (VPORTS)
The area in which the program can pan and zoom without regenerating the drawing.
Displays or does not display geometry (in a dimmed state) that is invisible for a visibility state. (BVMODE)
In a dynamic block, a custom property that allows only specified geometry to display in the block reference. (BVSTATE)
A collection of settings that control the display of edges and shading in a viewport.
A photorealistically rendered volume of space cast by the shadow of an object.
A closed 3D solid or mesh that has no gaps.
See world coordinate system (WCS).
A reference to one of the individual user interface elements that make up SteeringWheels. See also SteeringWheels.
Area of a SteeringWheel that is used to organize wedges and other buttons.
A section on the surface of a SteeringWheel that is designated for a specific navigation or orientation tool.
A reference to more than one of the individual user interface elements that make up SteeringWheels. See also SteeringWheels.
A rectangular area specified in the drawing area to select multiple objects at the same time. See also crossing selection, polygon window selection.
A polygonal area that masks underlying objects with the current background color. This area is bounded by the wipeout frame, which you can turn on for editing and turn off for plotting.
The representation of an object using lines and curves to represent its boundaries.
A drawing for manufacturing or building purposes.
A group of objects selected for in-place reference editing.
Another name for the XY plane of the user coordinate system. See also elevation and user coordinate system (UCS).
A set of menus, toolbars and dockable windows (such as the Properties palette, DesignCenter, and the Tool palettes window) that are grouped and organized so that you can work in a custom, task-oriented drawing environment.
A coordinate system used as the basis for defining all objects and other coordinate systems. See also user coordinate system (UCS).
Coordinates expressed in relation to the world coordinate system (WCS).
Behavior where the cursor wraps around the window and appears on the opposite side to allow the continuation of a drag operation instead of stopping at the edge of the drawing area.
See coordinate filters.
See external reference (xref).
To reduce or increase the apparent magnification of the drawing area. (ZOOM)