The Gb interface can use the FR protocol or the IP protocol. For different protocols, the configuration objects and principles of configuring the Gb interface links are different.
In Gb over FR mode, the NSE, BC, NSVC, and PTPBVC must be configured on the Gb interface links; in Gb over IP mode, the NSE, local NSVL, remote NSVL, and PTPBVC must be configured on the Gb interface links. Table 1 lists these objects.
Object |
Description |
|---|---|
Bearer channel (BC) |
A bearer channel for the frame relay. It is an E1/T1 timeslot group used to transfer data and signaling on the Gb interface. Bandwidth = number of timeslots x 64 kbit/s. One or more BCs can be configured on one E1. Each BC on an E1 is assigned a number to facilitate local management. This number is called BC ID. For an E1, the BC ID on the local end and the BC ID on the peer end can be different, but the timeslot distribution on both ends must be consistent. |
Network service virtual connection (NSVC) |
NSVC is the end-to-end virtual communication path between the BSC and the SGSN. The NSVC on the BSC side and the NSVC on the SGSN side have a one-to-one mapping relationship, and their NSVCIs are the same. NSVCs are divided into different groups at the NS layer. Each group is identified by an NSEI. The NSVCs in the same group use the loading sharing mode. If one NSVC is unavailable, the NS switches the data from this NSVC to another NSVC for transmission. A group of NSVCs are connected to one SGSN. In an FR network, an NSVC is mapped to a PVC. In an IP network, an NSVC is identified by a pair of IP addresses and UDP ports at both the BSS and the SGSN. |
Permanent virtual connection (PVC) |
PVC is the permanent virtual connection for the frame relay. It is a logical transmission channel. Multiple PVCs can be established on one BC. The PVCs are identified by Data Link Control Identifiers (DLCIs). The DLCI on the BSC side and that on the SGSN must be the same. The PVC is established with the NSVC. |
Network service entity (NSE) |
The NSE is represented by a BVC set at the BSSGP layer and an NSVC set at the NS layer. The NSE is uniquely identified by the NSEI. The NSEI on the BSC side and that on the SGSN side must be consistent. The FR protocol or the IP protocol is selected for one NSE. If the FR protocol is selected, the BC and NSVC should be configured. If the IP protocol is selected, the local and remote NSVLs should be configured. |
Local network service virtual link (NSVL) and remote NSVL |
The local NSVL determines the location of the GFGUG, establishes the mapping between the NSE and the device IP address/port number, and specifies the ports to transfer the data of the cells under the NSE. The remote NSVL establishes the mapping between the NSE and the device IP address/port number at the SGSN side, and determines the ports to transfer the data of the cells under the NSE. |
Point to point BSSGP virtual connection (PTPBVC) |
PTPBVC is the point-to-point virtual connection on the BSSGP layer. |
Figure 1 shows the logical connections between BSC and the SGSN at the NS layer and the BSSGP layer respectively.
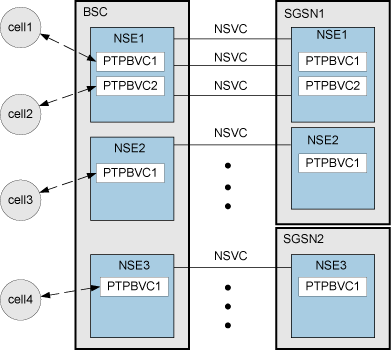
- As shown in Figure 1, an NSE is represented by a set of BVCs (a set of cells) at the BSSGP layer, and is represented by a set of NSVCs at the NS layer. The NS layer provides the BSSGP layer with data transmission channels. The data transmission channels of the cells under an NSE are selected from the NSVCs of the NSE to balance the traffic between NSVCs.
- In Gb over FR mode, you need to configure the NSVCs by specifying the BC and the NSVC; in Gb over IP mode, you need to configure NSVCs by specifying the local NSVL and the remote NSVL.
The principles of configuring the Gb interface links are as follows:
- One BSC can be connected to multiple SGSNs.
- One BSC can be configured with multiple NSEs.
- The NSE applies to the entire BSC instead of a single subrack.
- Two NSEs with the same NSEI on the BSC and on the SGSN are uniquely mapped to each other. Each PTPBVC and NSVC that belong to the same NSE on the BSC are uniquely mapped to a PTPBVC and an NSVC that belong to the mapping NSE on the SGSN respectively.
- When the SGSN pool function is disabled, a cell is configured with a PTPBVC, and the PTPBVC belongs to a specific NSE.
- When the SGSN pool function is enabled, a cell is mapped to multiple PTPBVCs, and these PTPBVCs must belong to different NSEs.
- In the case of direct point-to-point connections between the BSC and the SGSN, Huawei recommends that multiple timeslots on the E1 be bound to form a BC.
- The number of NSVCs that can be configured on one BC is not strictly limited. Huawei recommends that one BC be configured with one NSVC.
- The NSVCI configured on the BSC side must be consistent with the NSVCI configured on the SGSN side.