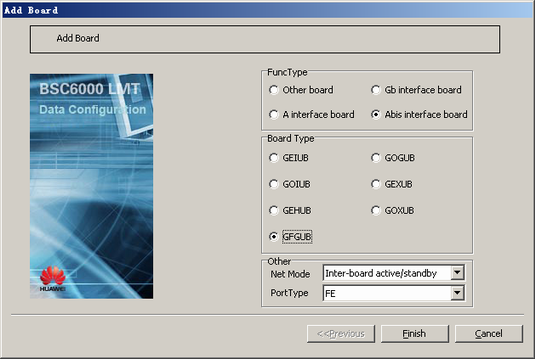
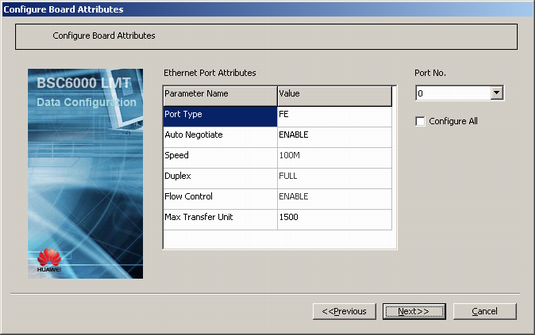
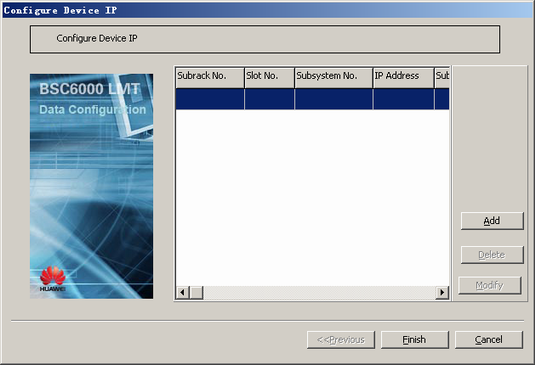
This describes how to add a GFGUB/GOGUB in the GMPS/GEPS and configure its attributes. The GFGUB/GOGUB is responsible for the IP transmission on the Abis interface.
| Scenario | BSC initial configuration and BSC capacity expansion |
| Mandatory/Optional | Optional. The GFGUB/GOGUB is configured when the Abis over IP mode is adopted. |
Prerequisite
The GMPS/GEPS has idle slots to hold the GFGUB/GOGUB.
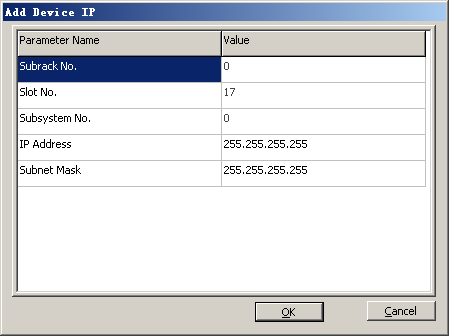
When the GFGUB/GOGUB is used to implement the Abis over IP mode, the device IP address and the port IP address must be configured. The device IP address and the port IP address can implement end-to-end communication separately.
You can choose the port IP address or device IP address for communication on the Software Parameter tab page of BSC Attributes.
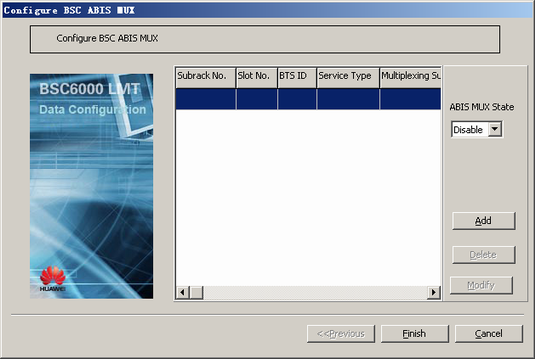
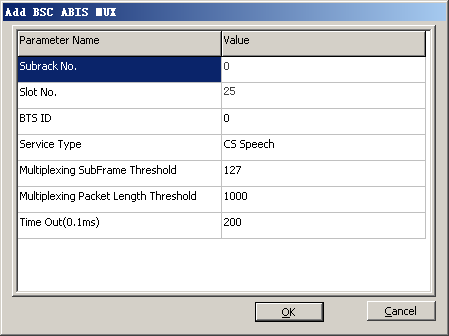
BSC ABIS MUX is optional. It is configured when the ABIS MUX is used to improve the IP transmission efficiency on the Abis interface. The ABIS MUX function is available for use only when the BTS in IP transmission mode is configured on the GFGUB, the PTU on this BTS is configured with the BTS ABIS MUX function, and the BSC ABIS MUX function is configured on the GFGUB.
When the BSC is configured with two GFGUB/GOGUBs, you can set Net Mode to Inter-Board Active/Standby or Inter-Board load sharing to improve networking reliability. When the BSC is configured with only one GFGUB/GOGUB (Independent mode), you can configure routes to guarantee networking reliability.
In active/standby mode, the IP addresses of related ports must be configured on the same network segment. In load sharing mode, if the BSC performs communication through device IP addresses, then the two boards for load sharing must use the same device IP address. Regardless of whether device IP addresses or port IP addresses are used for communication, port IP addresses must be on different network segments.
Besides the configuration of the networking mode, you can configure BFD link detection and ARP link detection to improve system reliability. You can either ARP link detection or BFD link detection on one port. ARP link detection is available when NEs at one end of the ARP link support the ARP link detection. BFD link detection, however, is available only when NEs at both ends of the BFD link support the BFD link detection.
Preparation
The following procedure takes how to configure a pair of active/standby GFGUBs in the GMPS as an example.
Parameter |
Example |
Source |
|
|---|---|---|---|
Subrack No. |
0 |
BSC internal planning |
|
Slot No. |
25 |
BSC internal planning |
|
Board Type |
GFGUB |
BSC internal planning |
|
Net Mode |
Inter-board active/standby |
BSC internal planning |
|
Port Type |
FE |
BSC internal planning |
|
Load Key |
Server |
BSC internal planning |
|
Device IP address |
IP Address |
172.16.125.156 |
Negotiation with the peer end |
Subnet Mask |
255.255.255.0 |
Negotiation with the peer end |
|
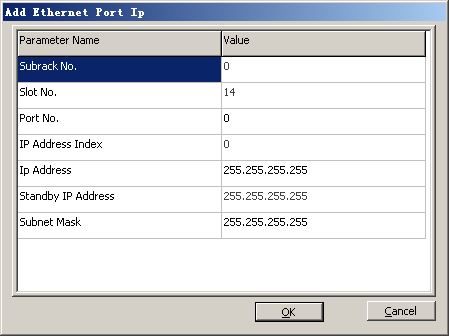
Port IP address |
Port No. |
0 |
Negotiation with the peer end |
IP Address Index |
0 |
Negotiation with the peer end |
|
Ip Address |
172.16.5.156 |
Negotiation with the peer end |
|
Standby Ip Address |
172.16.5.157 |
Negotiation with the peer end |
|
Subnet Mask |
255.255.255.0 |
Negotiation with the peer end |
|
BSC route |
Destination IP Address |
172.20.6.0 |
Negotiation with the peer end |
Subnet Mask |
255.255.255.0 |
Negotiation with the peer end |
|
Gateway IP Address |
172.16.5.153 |
Negotiation with the peer end |
|
BFD detection |
Port No. |
0 |
BSC internal planning |
IP Address Index |
0 |
Negotiation with the peer end |
|
Peer IP |
172.16.5.158 |
Negotiation with the peer end |
|
ARP link detection |
Port No. |
0 |
BSC internal planning |
IP Address Index |
0 |
Negotiation with the peer end |
|
Peer IP Address |
172.16.5.159 |
Negotiation with the peer end |
|
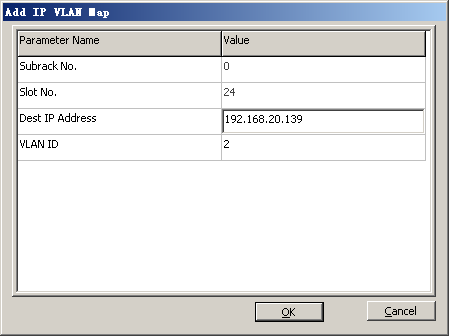
Mapping between the IP address and the VLAN |
Dest IP Address |
12.1.1.10 |
Negotiation with the peer end |
VLAN ID |
2 |
Negotiation with the peer end |
|
BSC ABIS MUX |
Service Type |
CS Data |
Negotiation with the peer end |
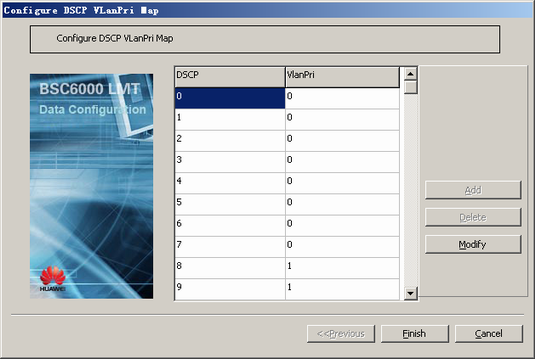
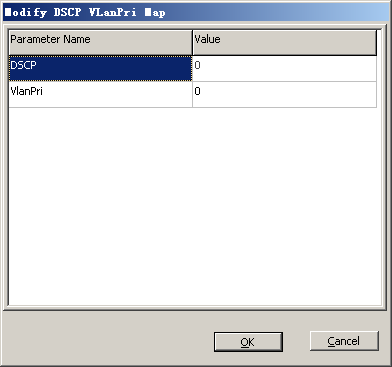
Dscp Vlanpri Map |
DSCP |
0 |
BSC internal planning |
VlanPri |
0 |
BSC internal planning |
|
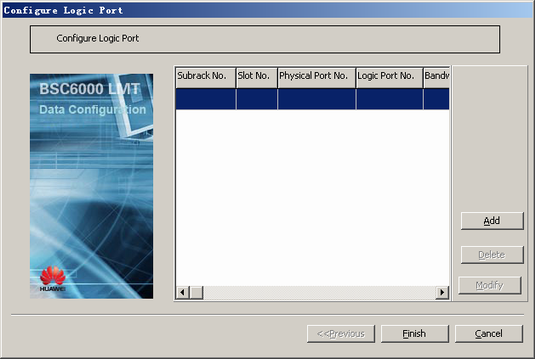
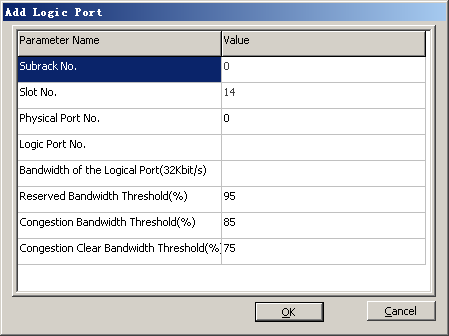
Logical port |
Logical Port No. |
0 |
BSC internal planning |
Bandwidth of the Logical Port(32Kbit/s) |
10 |
BSC internal planning |
|
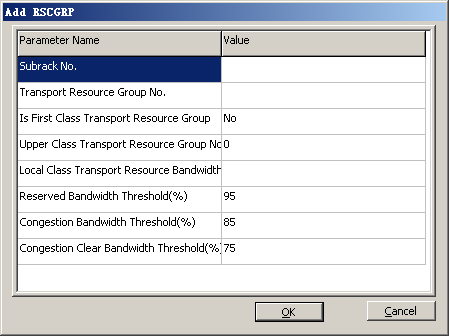
RSCGRP |
Subrack No. |
0 |
BSC internal planning |
Transport Resource Group No. |
0 |
BSC internal planning |
|
Is First Class Transport Resource Group |
Yes |
BSC internal planning |
|
Local Class Transport Resource Bandwidth (Kbit/s) |
10 |
BSC internal planning |
|
IP path |
IP Path ID |
0 |
BSC internal planning |
Site ID |
0 |
BSC internal planning |
|
IP Path Type |
CS |
BSC internal planning |
|
Transport Resource Bandwidth (Kbit/s) |
10 |
BSC internal planning |
|
Carry Flag |
Logical port |
BSC internal planning |
|
Logical Port No. |
0 |
BSC internal planning |
|
Procedure
- Add a board.
- Configure the board attributes.
- Configure the device IP address.
- Configure the port IP address.
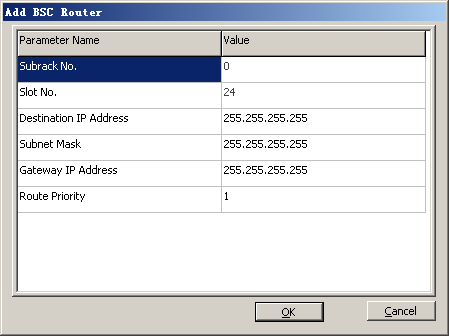
- Configure the BSC route.
- Optional: Configure port link detection.
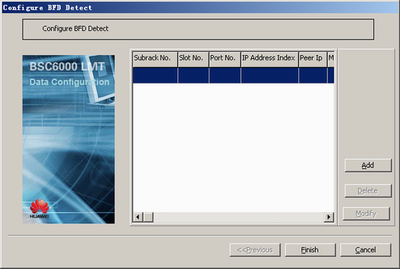
- Configure the BFD detection.
- Right-click GFGUB, and then choose from the shortcut menu. A dialog box is displayed, as shown in Figure 11.
 NOTE:
NOTE: - BFD detection and ARP link detection cannot be enabled at the same time.
- One port can be configured with only one detection mode. When a port is not configured with BFD detection or ARP link detection, physical layer detection is performed.
- Currently, you can configure detection modes in the following ways: BFD detection for both the active and standby ports, ARP link detection for both the active and standby ports, BFD detection for the active port and physical layer detection for the standby port, ARP link detection for the active port and physical layer detection for the standby port, and physical layer detection for both the active and standby ports.
- When configuring BFD link detection, you cannot configure the local description character, which is set to 1 by default.
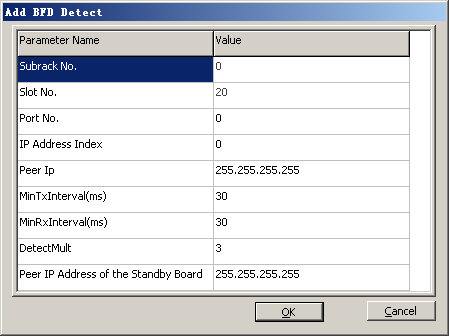
- Click Add. A dialog box is displayed, as shown in Figure 12.
- Set the parameters by referring to Table 1.
 NOTE:
NOTE: - The selected Port No. must be configured with the port IP address.
- Peer Ip must be different from the device IP address and the port IP address, and must be on the same network segment as the port IP address.
- In active/standby mode, Peer IP Address of the Standby Board can be configured and must be located on the same network segment as the corresponding port IP address. Peer IP Address of the Standby Board must be different from the device IP address and the port IP address but can be the same as Peer IP.
- In independent mode and load sharing mode, Peer IP Address of the Standby Board cannot be configured.
- Click OK to return to the dialog box, as shown in Figure 11.
- Click Finish. The configuration of the BFD detection is complete.
- Right-click GFGUB, and then choose from the shortcut menu. A dialog box is displayed, as shown in Figure 11.
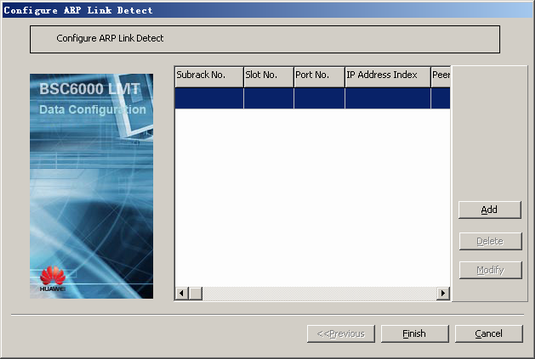
- Configure ARP link detection.
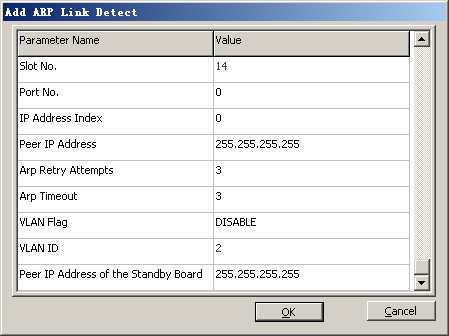
- Right-click GFGUB, and then choose from the shortcut menu. A dialog box is displayed, as shown in Figure 13.
- Click Add. A dialog box is displayed, as shown in Figure 14.
- Set the parameters by referring to Table 1.
 NOTE:
NOTE: - One port can be configured with only one ARP/BFD detection.
- The selected port and IP address index must be configured with a port IP address.
- Peer IP Address must be different from the device IP address and the port IP address that are configured on the BSC.
- Peer IP Address must be located on the same network segment as the selected Port No. and IP Address Index.
- In active/standby mode, Peer IP Address of the Standby Board can be configured and must be located on the same network segment as the corresponding port IP address. Peer IP Address of the Standby Board must be different from the device IP address and the port IP address but can be the same as Peer IP Address.
- In independent mode and load sharing mode, Peer IP Address of the Standby Board cannot be configured.
- Click OK to return to the dialog box, as shown in Figure 13.
- Click Finish. The configuration of the ARP link detection is complete.
- Configure the BFD detection.
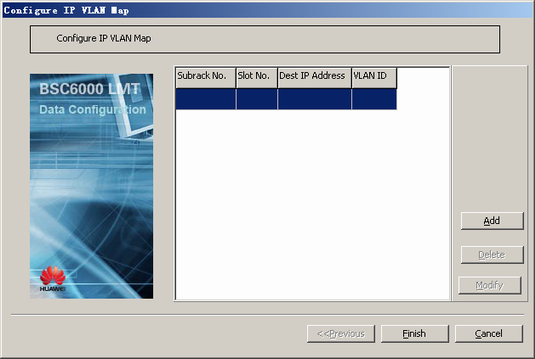
- Optional: Configure the IP-VLAN mapping.
- Optional: Configure the BSC ABIS MUX function.
- Optional: Configure the mapping relation between VLAN priority and DSCP.
- Optional: Configure a logical port.
- Optional: Configure a resource group.
- Optional: Configure the IP path.