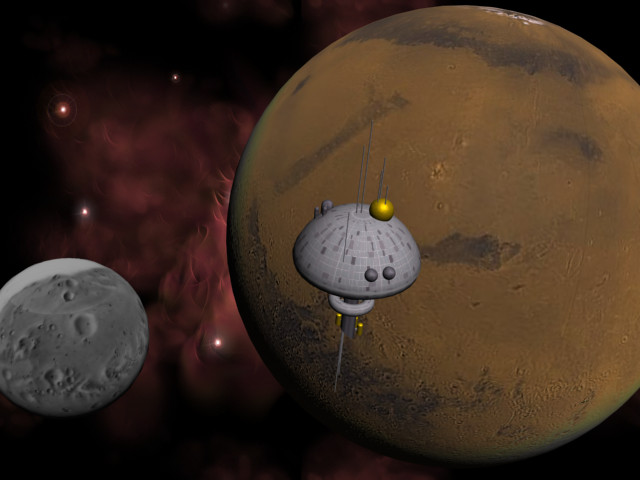

So far, you've used dummy objects to help animate the spacefighters. Another handy use of dummy objects is as an alternate pivot point. Any object can be used as a pivot, but dummies are great because they don't render.
Set up the lesson:
Files for this lesson are in the tutorials\intro_to_animation folder.
This scene includes the following:
Take a few moments to familiarize yourself with the names of the objects in the scene. This will make it easier for you to select objects during this lesson.
Rotate Mars and its moons:
The first part of this lesson focuses on the three heavenly bodies you see in the scene. You will set up a dummy object to control the rotation of Mars and its moons, Deimos and Phobos.
Make the dummy a little larger than the planet so it's easier to pick.
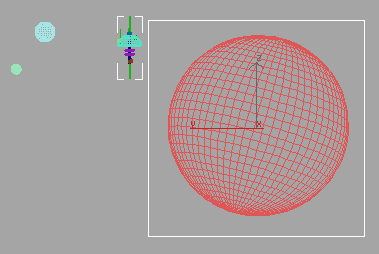
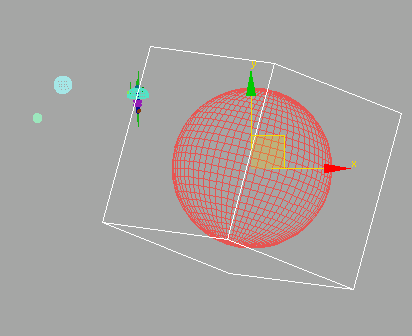
MarsControl is now aligned and oriented with the center of Mars.
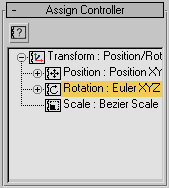
 Click
the Assign Controller button and choose TCB Rotation then click
OK.
Click
the Assign Controller button and choose TCB Rotation then click
OK.TCB Rotation will allow you to rotate objects on their Local axes as opposed to the World axes. This is beneficial when you have an object that is rotating on an axis that is tilted, such as the rotational axis of a planet.
 Select Mars,
then click Select and Link. Drag the rubber band to MarsControl.
Release the mouse button when the cursor changes.
Select Mars,
then click Select and Link. Drag the rubber band to MarsControl.
Release the mouse button when the cursor changes. Link
each of the moons, Deimos and Phobos, to MarsControl.
Link
each of the moons, Deimos and Phobos, to MarsControl.Mars and its two moons are now linked to MarsControl. Any movement or rotation you make to MarsControl will affect all the planetary bodies.
 Click
Select And Rotate, and select MarsControl.
Click
Select And Rotate, and select MarsControl. Change
the Reference Coordinate System from View to Local.
Change
the Reference Coordinate System from View to Local. Turn
on the Auto Key button and move the time slider to frame 100.
Turn
on the Auto Key button and move the time slider to frame 100.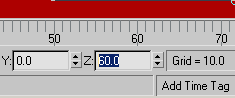
This rotates MarsControl by 60 degrees around its local Z axis. Because the planet and moons are linked to MarsControl, they also rotate.
You will see Mars rotating on its axis, then at frame 60, Deimos swings into view and passes by and Phobos remains off-camera. If you like, you can zoom out to see both moons during playback.
Set the space station into orbit:
Now that Mars is spinning on its own axis and Deimos and Phobos are orbiting Mars, you can set the space station into a geosynchronous orbit around Mars (an orbit that matches the planet's rotation). You'll use the same technique for controlling the space station.
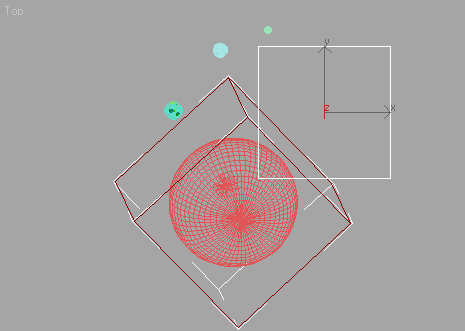
It doesn't matter where you place the dummy object, because you'll align it to Mars in a few steps.
 Click
the Assign Controller button, and choose TCB Rotation. Click OK.
Click
the Assign Controller button, and choose TCB Rotation. Click OK.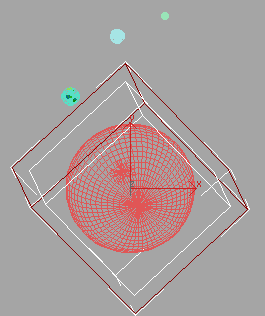
These are the same settings you made when aligning MarsControl to Mars in the previous section.
 In the
Left viewport, link SpaceStation to StationControl.
In the
Left viewport, link SpaceStation to StationControl. Turn
on Select And Rotate and select StationControl.
Change the Reference Coordinate System from View to Local, if it's
not already changed.
Turn
on Select And Rotate and select StationControl.
Change the Reference Coordinate System from View to Local, if it's
not already changed. Turn
on the Auto Key button and move the time slider to frame 100.
Turn
on the Auto Key button and move the time slider to frame 100.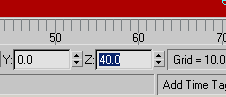
To create
an incrementally saved file, use the Save As command click the  button.
button.
Now the Space Station is orbiting around Mars but it's orbiting at a slower rate.
Add artificial gravity to the space station:
The space station needs to rotate around its own axis in order to generate some level of artificial gravity for its personnel. This last section will solve that problem.
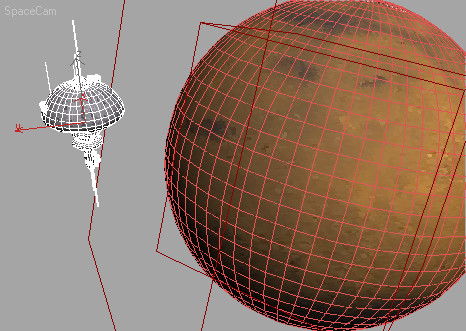
 Click
the Assign Controller button and choose TCB Rotation then click
OK.
Click
the Assign Controller button and choose TCB Rotation then click
OK. Turn
on Select And Rotate if it's not already active. Set the Reference Coordinate
System from View to Local.
Turn
on Select And Rotate if it's not already active. Set the Reference Coordinate
System from View to Local.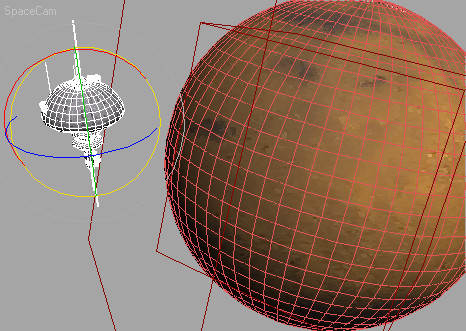
 Turn
on the Auto Key button and move the time slider to frame 100.
Turn
on the Auto Key button and move the time slider to frame 100.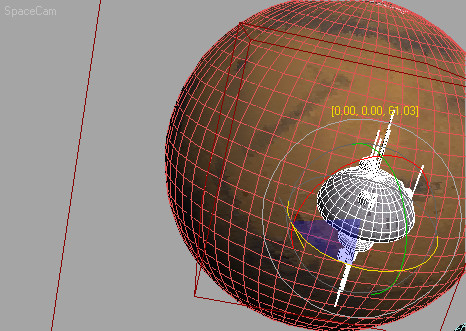
Now the Space Station rotates about its own axis while it's in geosynchronous orbit around Mars. Maximize the SpaceCam viewport for a better view.