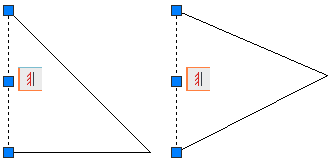
A vertical constraint forces lines of pairs of points to remain parallel to the Y-axis of the current UCS.
In the example below, a vertical constraint has been applied to the triangle on the left. The result is the block definition on the right, where the constrained line is vertical to the current UCS.
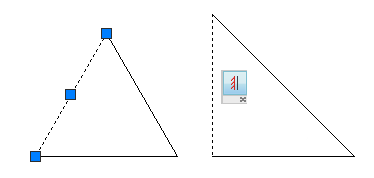
Manipulate a Vertical Constraint
When you manipulate a block with a vertical constraint applied, the constrained line or points will always remain vertical to the UCS.
In the example below, a vertical constraint has been applied to the triangle on the left. The geometry of the triangle on the right has been changed, but the constrained line remains vertical.