Using Raytrace Materials and Maps

Introduction to Materials and Mapping

Using Displacement Mapping with Surface Properties

Texturing the Chessboard
In
Modeling a Chess Set
,
you learned how to create the pieces for a chess set. Chess pieces
want to live on a chessboard. In this tutorial, you'll construct
a chessboard that has a wood-grained, checkerboard pattern. You'll also
add shininess and reflection to the chessboard.
- The
files for this lesson can be found in the tutorials/intro_to_materials folder.
Set
up the lesson:
- Load
the file tut_knight.max.
Create
the chessboard:
-

 On the
Create panel, click the Geometry button. Make sure Standard Primitives
is chosen in the drop-down list.
On the
Create panel, click the Geometry button. Make sure Standard Primitives
is chosen in the drop-down list. - Click
the Box button.
-
 If 2D
Snap is on, turn it off.
If 2D
Snap is on, turn it off. - In
the Top viewport, drag to set the initial length and width of the
box, then release the mouse and drag downward to set an initial height.
Click to finish.
Don't worry about the initial dimensions: you
will change them soon.
- Rename
the box chessboard.
- In
the box's Parameters rollout, set the Length and Width to both equal 32cm,
and set Height equal to –1cm.
TipBecause
the board is bigger than the chess pieces, you might need to zoom
viewports and move either object before you can comfortably see
both of them together.
- Use
the Move tool to position the box at the world origin: 0,0,0.
Create
the squares:
-
 Activate
the Perspective viewport and click the Zoom Extents button.
Activate
the Perspective viewport and click the Zoom Extents button. -
 Click
the Field Of View button and zoom in so the chessboard fills the
viewport.
Click
the Field Of View button and zoom in so the chessboard fills the
viewport. -
 On the
toolbar, open the Material Editor by clicking the Material Editor
button or use the M keyboard shortcut.
On the
toolbar, open the Material Editor by clicking the Material Editor
button or use the M keyboard shortcut. - Click
the first sample sphere and click the map button just to the right
of the Diffuse color swatch.
The Material/Map Browser appears.
- In
the Material/Map Browser, double-click Checker.
3ds Max has
a built-in checker pattern, which makes your work easier. The active
sample slot now shows a sphere with the checker pattern.
-

 In the
Material Editor, click Assign Material To Selection, then click
Show Map In Viewport.
In the
Material Editor, click Assign Material To Selection, then click
Show Map In Viewport.This lets you see the map in shaded viewports.
(The viewport display of maps is only an approximate.)
The default checker pattern is two by two, but
a chessboard needs eight squares in each direction.
NoteIf the checker pattern looks slightly skewed,
right-click the Perspective viewport label and turn on Texture Correction.
- On
the Coordinates rollout, set both the U and V Tiling values to 4.0.
Now the board has the right number of squares.
If you render the Perspective viewport, you
see that the checker pattern is more refined than the shaded viewport
shows.
NoteBecause
the chessboard is made out of a box, the checker pattern is also
applied to the sides. Since the chessboard is so thin, the pattern on
the sides isn't obvious.
Give
the checker pattern a wood texture:
-
 Open
the Utilities panel and click Asset Browser.
Open
the Utilities panel and click Asset Browser.The Asset Browser appears. Click OK to the copyright
advisory it displays.
- The
Asset Browser is a large dialog. Move and resize it so you can see
both it and the Material Editor.
- Use
the navigation tree at the left of the Asset Browser window to locate
the tutorials/intro_to_materials folder.
- In
the Material Editor, make sure the Checker map's Checker Parameters
rollout is visible.
- In
the Asset Browser, locate the file Oak1.tga.
Drag the Oak1.tga thumbnail to the Color
#1 map button on the Checker Parameters rollout. Then drag the Walnut3.tga thumbnail to the Color
#2 map button.
- Close
the Asset Browser.
Now if you render the chessboard, it has a contrasting
wood pattern.
- Save
the scene as mychessboard.max.
Add
polish to the chessboard:
-
 In the
Material Editor, click the Go To Parent button.
In the
Material Editor, click the Go To Parent button. - Open
the Maps rollout.
- Click
the map button for the Reflection map component.
The Material/Map Browser opens.
- Double-click
the Flat Mirror map.
- Render
the scene.
The pieces are reflected in the chessboard,
but the wood grain is washed out.
-
 Click
the Go To Parent button and, on the Maps rollout, change the Reflection
Amount to 30.
Click
the Go To Parent button and, on the Maps rollout, change the Reflection
Amount to 30.The wood grain is not as washed out as before
but still looks faded.
- On
the Maps rollout, click the Checker map in the Diffuse Color component.
- In
the Checker Parameters rollout, click the Color #1 map and open
the Output rollout.
- Set
the Output Amount to 1.5.
-
 Click
the Go Forward To Sibling button and make the same change to the
Output Amount of the Color #2 map.
Click
the Go Forward To Sibling button and make the same change to the
Output Amount of the Color #2 map. - Render
the scene.
The wood grain looks much warmer and more realistic.
- Save
the scene as mychessboard01.max.


 On the
Create panel, click the Geometry button. Make sure Standard Primitives
is chosen in the drop-down list.
On the
Create panel, click the Geometry button. Make sure Standard Primitives
is chosen in the drop-down list. If 2D
Snap is on, turn it off.
If 2D
Snap is on, turn it off. Activate
the Perspective viewport and click the Zoom Extents button.
Activate
the Perspective viewport and click the Zoom Extents button. Click
the Field Of View button and zoom in so the chessboard fills the
viewport.
Click
the Field Of View button and zoom in so the chessboard fills the
viewport. On the
toolbar, open the Material Editor by clicking the Material Editor
button or use the M keyboard shortcut.
On the
toolbar, open the Material Editor by clicking the Material Editor
button or use the M keyboard shortcut.

 In the
Material Editor, click Assign Material To Selection, then click
Show Map In Viewport.
In the
Material Editor, click Assign Material To Selection, then click
Show Map In Viewport.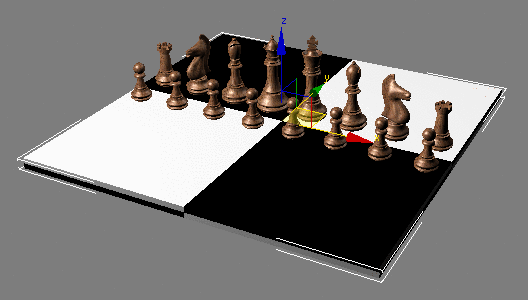

 Open
the Utilities panel and click Asset Browser.
Open
the Utilities panel and click Asset Browser.
 In the
Material Editor, click the Go To Parent button.
In the
Material Editor, click the Go To Parent button.
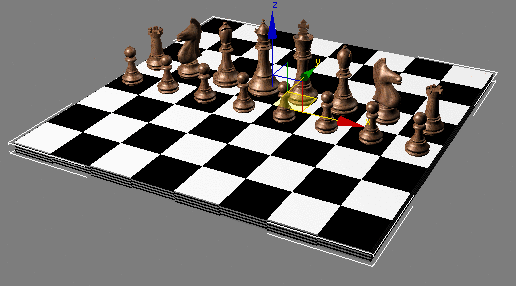
 Click
the Go To Parent button and, on the Maps rollout, change the Reflection
Amount to 30.
Click
the Go To Parent button and, on the Maps rollout, change the Reflection
Amount to 30.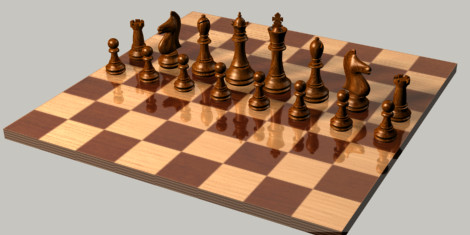
 Click
the Go Forward To Sibling button and make the same change to the
Output Amount of the Color #2 map.
Click
the Go Forward To Sibling button and make the same change to the
Output Amount of the Color #2 map.